Area of the Enclosed Octagon?
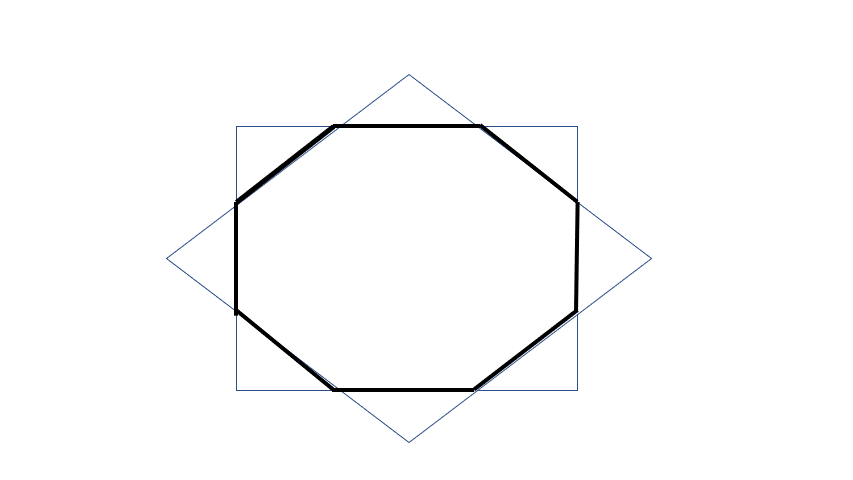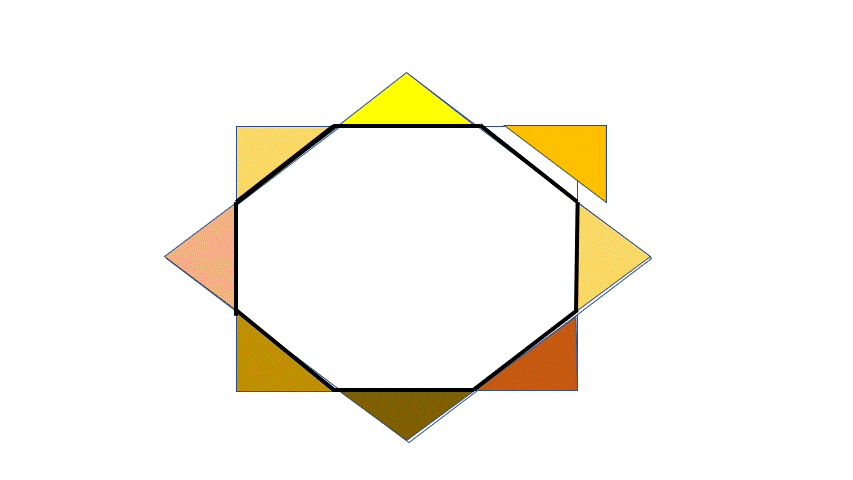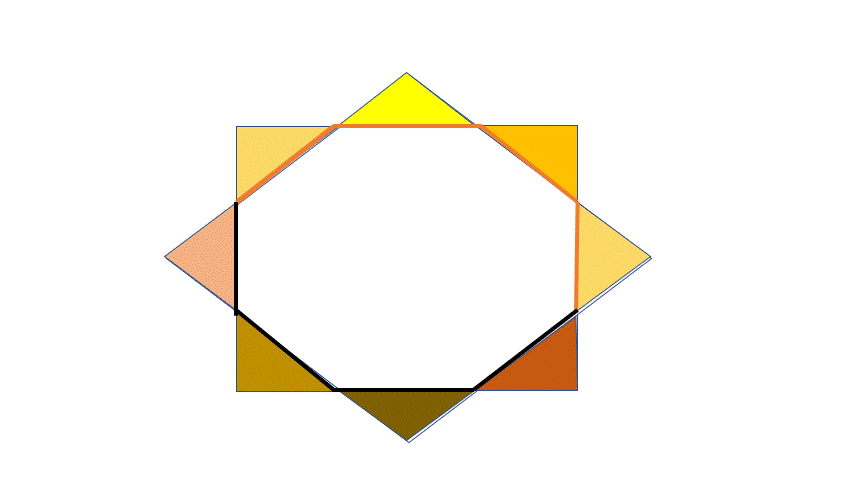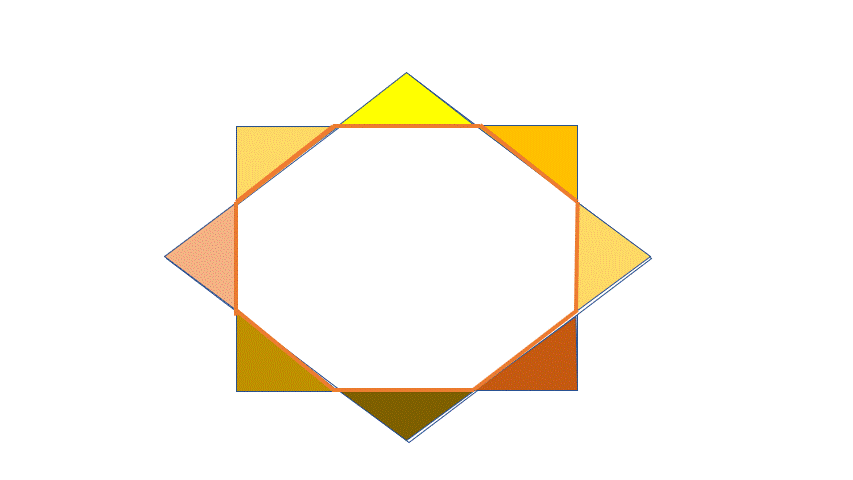
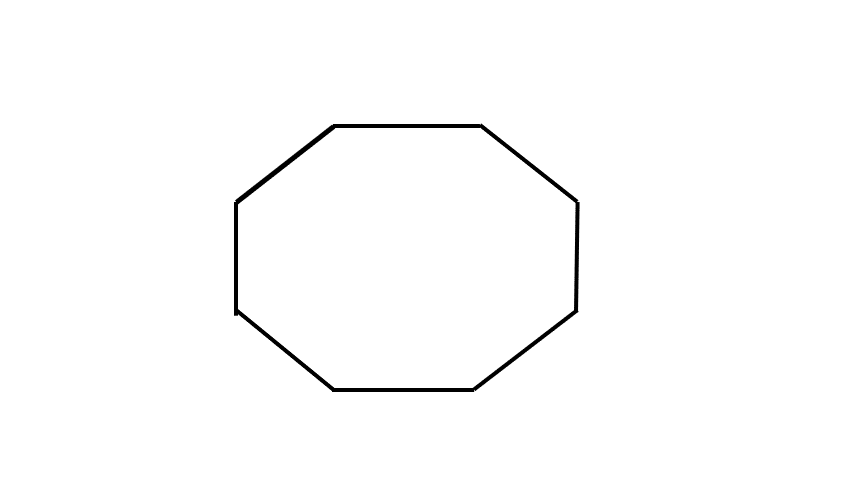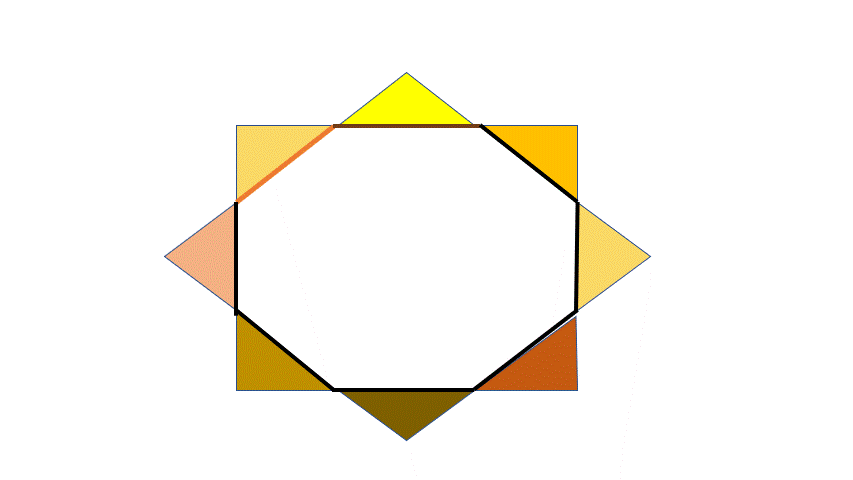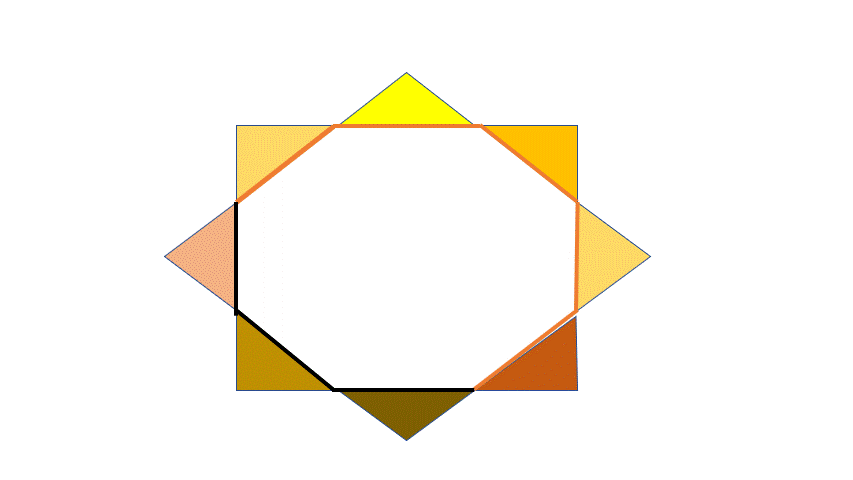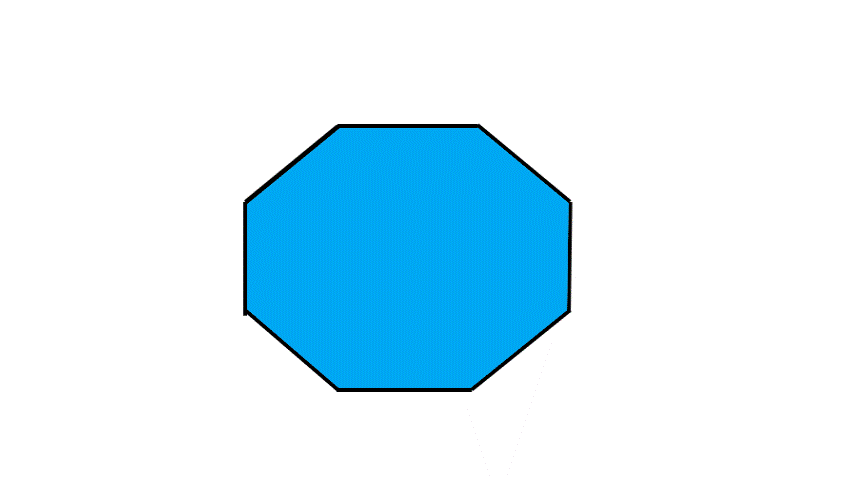 The figure above shows two squares of area
9
of the same center. what is the area of the enclosed octagon rounded to two decimal places or to the nearest hundredth?
The figure above shows two squares of area
9
of the same center. what is the area of the enclosed octagon rounded to two decimal places or to the nearest hundredth?
The answer is 7.46.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
Thank you for sharing your solution.
@nibedan mukherjee , is it better now?
Log in to reply
Geometry is a very fascinating wing of mathematics...
Log in to reply
For sure it is. Absolutely no doubt about that. I have a YouTube channel with some videos as well. You might like them. Here's the channel link
Log in to reply
@Mahdi Raza – I have already seen them.. gr8 work keep it up.
Log in to reply
@Nibedan Mukherjee – Ohh, great! Thank you so much Nibedan, nice talking to you!!
Log in to reply
@Mahdi Raza – Pleasure to know you too!.. To know more about me google "Nibedan Mukherjee" . Cheers!
now it's perfect.. @Mahdi Raza ...
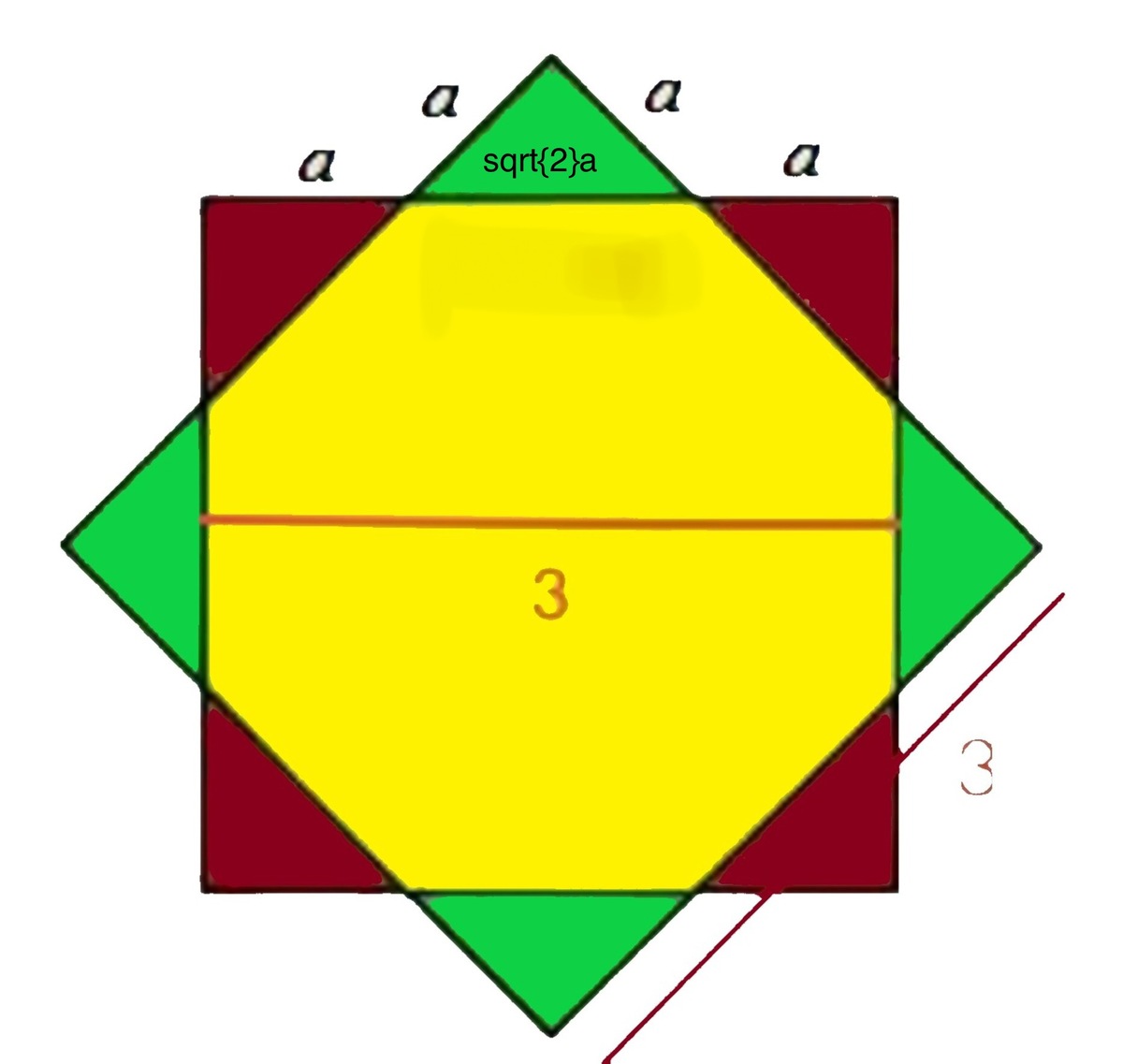
All the Red and Green triangles are congruent and Right -isosceles due to symmetry. The squares each has an area of 9 , thus the side of the square is 3 . The hypotenuse of each small triangle is 2 a .
We have now 2 a + 2 a = 3 ⟹ a = 2 + 2 3 .
The area of two Red triangles = area of one small Red square of side a = a 2 = ( 2 + 2 3 ) 2
The area of the octagon is: Area of the Big square- area of the 4 Red triangles =
Area of the Big square of side 3 - area of two Red squares of side a =
9 − 2 ( 2 + 2 3 ) 2 = 7 . 4 6 .
@Hana Wehbi Square root over '2' only not over variable 'a' , please do check it...
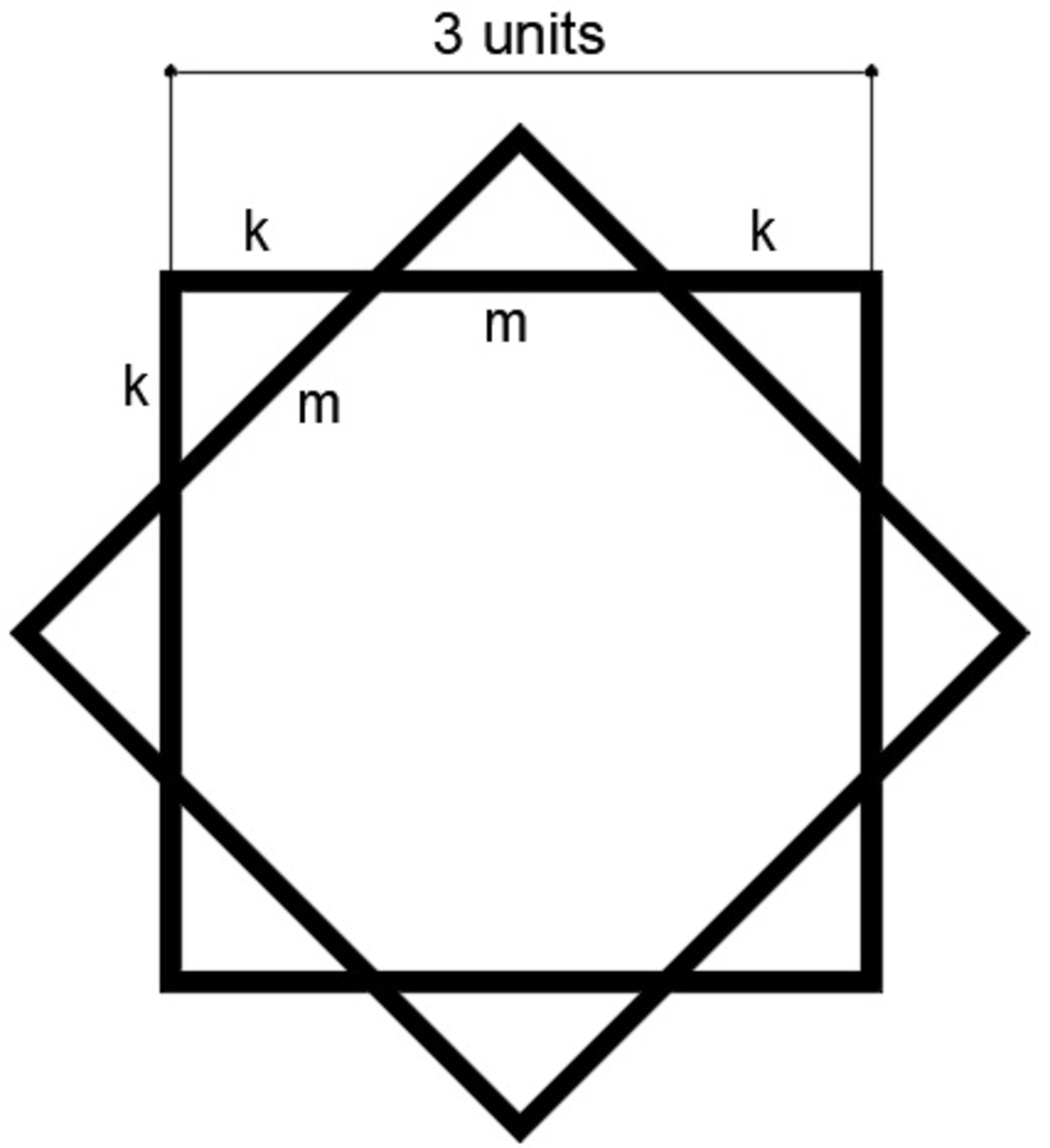 Consider my figure above. The side length of the square is
9
=
3
, so
Consider my figure above. The side length of the square is
9
=
3
, so
2 k + m = 3 [equation 1]
Applying pythagorean theorem on the small right triangle on the corner of the square, we have the equation
m = k 2 [equation 2]
The area of the regular octagon is equal to the area of the square minus the area of the four small right triangles. The area of one triangle is
A T = 2 1 k 2
So we need to find k 2 , substituting the value of m in equation 1 into equation 2 we get
k = 2 + 2 3
Squaring k , we get
k 2 = 6 + 4 2 9
Now, substitute
A T = 2 1 k 2 = 2 1 × 6 + 4 2 9 = 1 2 + 8 2 9
So the area of the 4 small right triangles is
4 × A T = 1 2 + 8 2 4 × 9 = 1 2 + 8 2 3 6
Now, the area of the regular octagon is
A o c t a g o n = 9 − 1 2 + 8 2 3 6 ≈ 7.46 square units answer
A = 9 − 4 × 2 1 x ⋅ x A = 9 − 1 . 5 4 = 7 . 4 5 8