Circle-ception
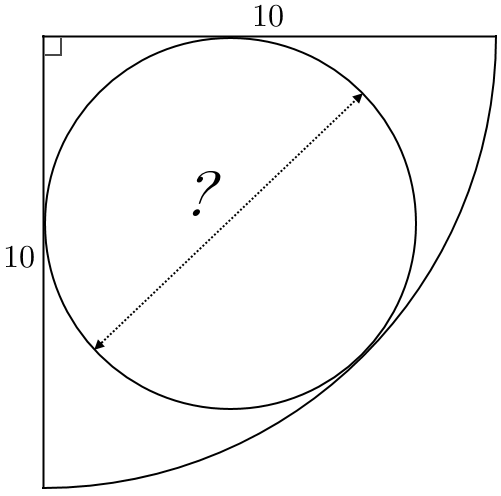 A quadrant of a circle of radius
1
0
has a circle inscribed in it - its diameter can be written as
a
(
b
−
c
)
in fully factorised form, where
b
is square free and
a
,
b
and
c
are integers.
A quadrant of a circle of radius
1
0
has a circle inscribed in it - its diameter can be written as
a
(
b
−
c
)
in fully factorised form, where
b
is square free and
a
,
b
and
c
are integers.
Find the value of ⌊ a + b + c a 2 b 2 c 2 ⌋ .
The answer is 69.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
nice problem but don't you think if the main aim of this problem was to find the radius of the circle inside, you could have asked just asked a+b+c instead of a largest integer function...just a minor point rather
The value is 69.56 approx.
If you round it off, the answer should be 70
Log in to reply
We are dealing with floor functions here.
Log in to reply
Correct. ⌊ 6 9 . 5 6 ⌋ = 6 9 because it is the greatest integer that is less than or equal to x. If the answer was 7 0 , I would have asked for the nearest integer, or the ceiling function (the smallest integer that is greater than or equal to x): ⌈ 6 9 . 5 6 ⌉ = 7 0 .
More on floor/ceiling functions here .
Log in to reply
@Michael Fuller – It was Vasudev who raised that problem not me. I know the concept of the floor function. :)
@Michael Fuller – Thanks for the link, I had never heard of floor functions before!
Awesome answer...
awesome solution (y)
Exactly Same Method
It is a bit unclear that the sign meant floor function.
Assume a chord is drawn from point of the right angle R through centre of the circle and it meets the circle at point P and Q and the tangent from the point R meets at T, then RP.RQ=RT^2. If radius is x, then RT =x, RQ=10 and RP=10-2x; Hence 10*{10-2x}=x^2 or x=10{2^0.5 -1 }
r + r 2 = 1 0 , r is the radius of the inscribed circle.
Solve for r and multiply by 2 to find the diameter.
The two points where the circle tangentially touches the quadrant's sides must be the same distance away from the top left corner. So a right isosceles triangle can be formed.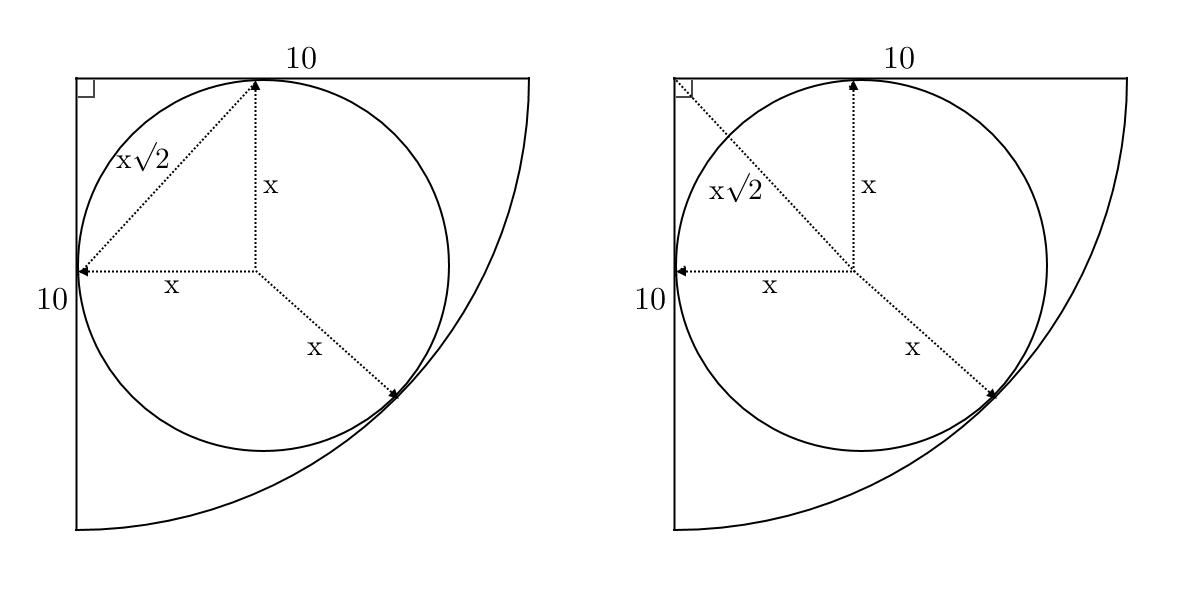
Let the radius of the incircle be x . As shown by the first diagram, the right isosceles triangle has legs x and therefore hypotenuse x 2 . In the second diagram, we see that x 2 + x = 1 0 (the radius of the quadrant).
x + x 2 = 1 0 x ( 1 + 2 ) = 1 0 x = 1 + 2 1 0
As the diameter of the circle is 2 x , it is equal to 1 + 2 2 0 , which after the denominator is rationalised comes to 2 0 2 − 2 0 ≡ 2 0 ( 2 − 1 ) . So a = 2 0 , b = 2 , c = 1 .
⌊ 2 0 + 2 + 1 2 0 2 × 2 2 × 1 2 ⌋ = ⌊ 2 3 1 6 0 0 ⌋ = ⌊ 6 9 + 2 3 1 3 ⌋ = 6 9