Coating in Lenses!
To ensure almost 1 0 0 % transmittivity, photographic lenses are often coated with a thin layer of dielectric material. The refractive index of this material is intermediated between that of air and glass (which makes the optical element of the lens). A typically used dielectric film is M g F 2 ( n = 1 . 3 8 ) . What should the thickness of the film ( d in Angstrom) be so that at the center of the visible spectrum ( 5 5 0 0 A n g s t r o m ) , there is maximum transmission?
Note : Round off the value of d to the nearest 1000. (ex. if the value comes out to be 5997, then the answer should be 6000)
Source - NCERT Exemplar Problems
The answer is 1000.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
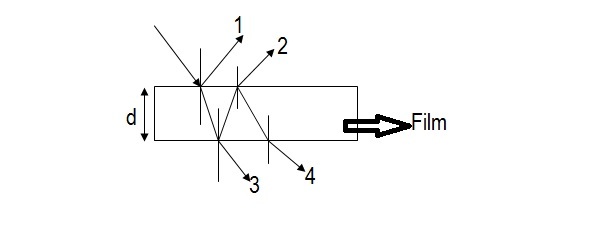
hope u r reading this
Path difference between ray 1 and 2
Δ x = 2 μ f i l m d cos r + 2 λ
path difference between ray 3 and 4
Δ x = 2 μ f i l m d cos r
r is angle of refraction.
For maximum transmission c o s r = 1 so r = 0 o and of course Δ x = n λ
Shouldn't the case of 3 and 4 be considered during transmission.
so by this we get
2 μ f i l m d = λ for n = 1
d = 2 × 1 . 3 8 5 5 0 0
d = 1 9 9 2 . 7 a n g s t r o m and according to question rounding off gives 2000
but the answer you posted, is get by using path difference between 1 and 2
Why is it so, plz correct me if i am wrong and do reply
@Nishant Rai do reply
Log in to reply
@Tanishq Varshney Check the solution i have posted. This is what NCERT has provided.
Log in to reply
ok but plz do consider by statement , see the diagram above i posted , during transmission ray 3 and 4 will come out, correct??
Log in to reply