Cone you sphere the time to solve this?
 If the largest possible volume of a cone inscribed in a sphere of unit volume can be represented as
b
a
, where
a
and
b
are coprime natural numbers, what is the value of
a
+
b
?
If the largest possible volume of a cone inscribed in a sphere of unit volume can be represented as
b
a
, where
a
and
b
are coprime natural numbers, what is the value of
a
+
b
?
The answer is 35.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Moderator note:
You have only shown that the extremal point of the volume occurs at x = 3 1 , but you did not show that it is a maximum point.
@Raj Magesh : NCERT type problem, eh?
Log in to reply
Yeah, I like optimization. XD
Log in to reply
Your title for this problem is very good! @Raj Magesh
Log in to reply
@Noel Lo – Haha, thanks. I try to be as punny as possible, though many want to strangle me for it. :P
External point? You mean the vertex or apex? x is parallel to the base. The circle x 2 + z 2 = r 2 is the base. y = r the radius of the base. The vertex is at ( − 1 , 0 ) , therefore the height h = x − ( − 1 ) = 1 + x and volume V = 3 π r 2 h = 3 π y 2 ( 1 + x ) = 3 π ( 1 − x 2 ) ( 1 + x ) . Therefore V = V ( x ) a function of x and maximum V ( x ) occurs when d x d V = 0 .
Log in to reply
To show that it's maximum, use the second derivative test and show that V max ′ ′ ( 3 1 ) < 0 .
Log in to reply
Thanks. Didn't notice it is "extremal". I thought it was "external".
Yeah, d x d V = 0 only implies that the point is either a point of maximum, a point of minimum or a point of inflection.
Log in to reply
Yes, I missed that step of showing d x d V < 0 . But actually, if you solve for d x d V = 0 ⇒ x = 3 1 and x = − 1 . When x = − 1 , V = 0 minimum, x = 3 1 V is maximum.
Log in to reply
@Chew-Seong Cheong – That's not enough proof, you have only shown that V ( 0 ) and V ( 3 1 ) are EXTREMAL points, and not min/max points.
Take y = x 3 as an example. At d x d y = 0 , does it mean that at x = 0 , it is min or max point? no! It's just an inflection point
p = 4 sin 2 θ ( 1 + cos θ )
Maximum p occurs at cos θ = 3 1 while sin θ = 3 8 :
Maximum p = 4 9 8 ( 1 + 3 1 ) = 9 2 3 4 = 2 7 8 = ( 3 2 ) 3 .
8 + 27 = 35
Answer: 3 5
Log in to reply
May you elaborate your solution.
What is p here? How did you reach to it? Thanks.
@Chew-Seong Cheong hey..so I'm assuming the x^2 + y^2 =1 circle is one of the Great-Circles of the Unit-Sphere which is why the cone (more specifically, that big isosceles triangle inside a cone) is inscribed within that circle. But since our sphere has a volume of 1, radius of that circle should be the cube root of (3/4π). But the equation of the circle says It's radius is 1. Can you please tell me if my assumption is correct. Thanks in anticipation.
Log in to reply
unit sphere means a sphere with radius 1.
Unit sphere does not mean that its volume is 1.
Log in to reply
Oh okay thank you. A 'sphere of unit volume' and a 'Unit Sphere' is the same thing right?
Log in to reply
@Todd Diez – no.
Unit volume = volume of numerical value of 1
Unit sphere = a Sphere where a radius of 1.
Argh... Unit volume... noooooooooooooooooooooooo....
Log in to reply
Yesssssssssssssss, the problem writer should have been more specific.
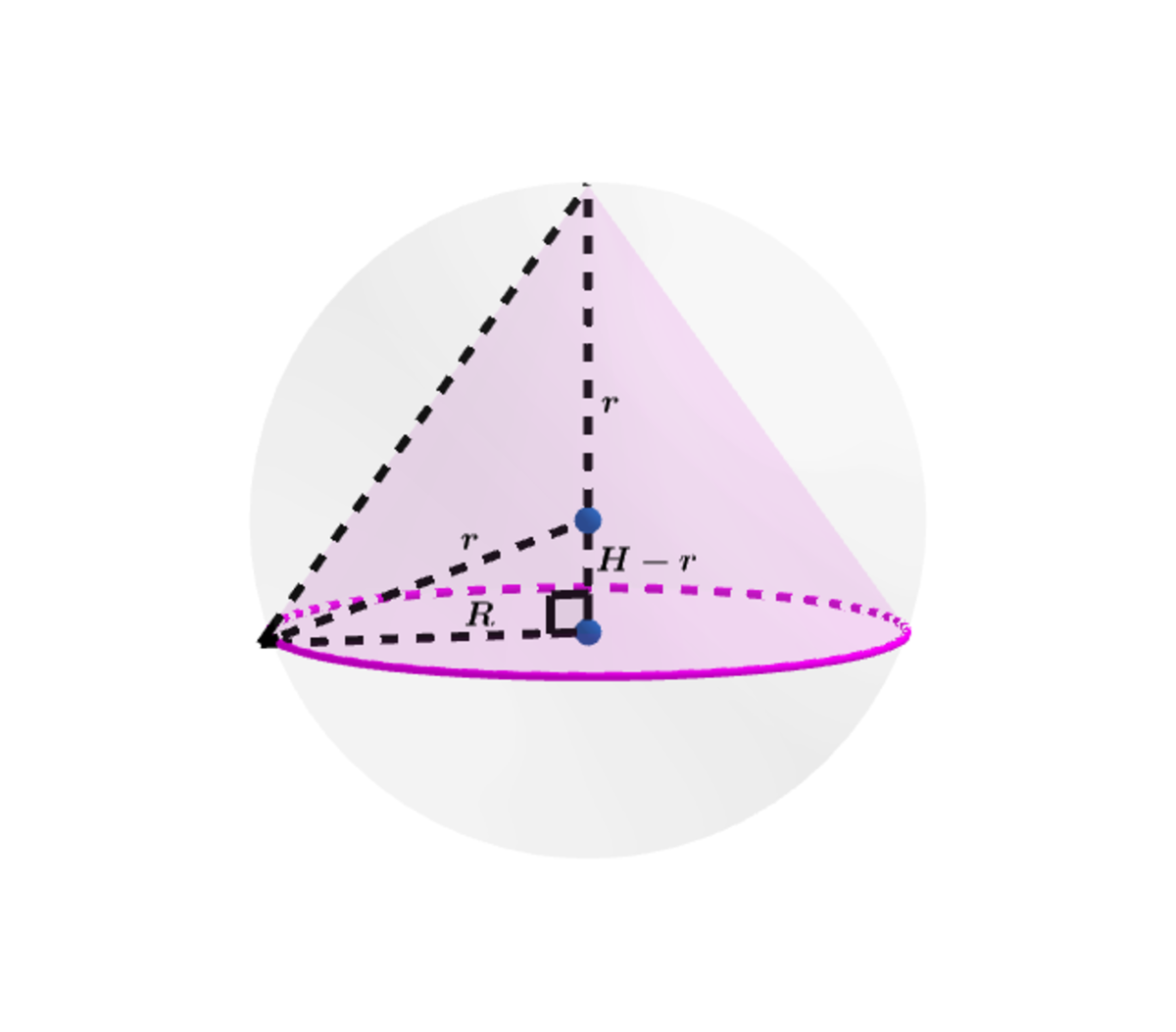
Let the volume of the sphere V s = 3 4 π r 3 and the volume of the cone V c = 3 1 π R 2 H .
From the geometry of the problem we have a right triangle with hypotenuse r and legs R and H − r
⟹ R 2 = r 2 − ( H − r ) 2 ⟹ V c = 3 1 π ∗ ( 2 H 2 r − H 3 ) ⟹
d H d V c = 3 1 H π ∗ ( 4 r − 3 H ) = 0 and H = 0 ⟹ H = 3 4 r
⟹ R 2 = 9 8 r 2 ⟹ R = 3 2 2 r
d H 2 d 2 V c ∣ H = 3 4 r < 0 ⟹ max at H = 3 4 r
∴ V c = ( 3 4 π r 3 ) ∗ 2 7 8 = V s ∗ 2 7 8
Since we have a unit sphere ⟹ V s = 1 ⟹ V c = 2 7 8 = b a ⟹ a + b = 3 5 .
Volume of a cone is given by: V = 3 1 π r 2 h , where r is the radius of the circular base and h the height. For a cone inscribed in a sphere, for a fixed r , the largest h and hence the largest V is when the cone is right circular.
Now consider a circle x 2 + y 2 = 1 . Let the vertex of the cone be ( − 1 , 0 ) and its base be parallel to the y -axis, hence r = y and h = 1 + x . Therefore, we have:
V ⇒ d x d V = 3 1 π r 2 h = 3 1 π y 2 ( 1 + x ) = 3 1 π ( 1 − x 2 ) ( 1 + x ) = 3 1 π ( 1 + x − x 2 − x 3 ) = 3 1 π ( 1 − 2 x − 3 x 2 )
d x d V ⇒ 1 − 2 x − 3 x 2 3 x 2 + 2 x − 1 ( 3 x − 1 ) ( x + 1 ) = 0 = 0 = 0 = 0
Since d x 2 d 2 V { < 0 , when x = 3 1 > 0 , when x = − 1 , V is maximum when x = 3 1 .
V m a x = 3 π ( 1 − ( 3 1 ) 2 ) ( 1 + 3 1 ) = 3 π ( 9 8 ) ( 3 4 ) = 8 1 3 2 π
V m a x is from a cone inscribed by a unit-radius sphere, therefore, the maximum volume of a cone inscribed by a unit sphere is:
V m a x ′ = 3 4 π V m a x = 3 4 π 8 1 3 2 π = 2 7 8 ⇒ a + b = 8 + 2 7 = 3 5