Confusing Wedge!
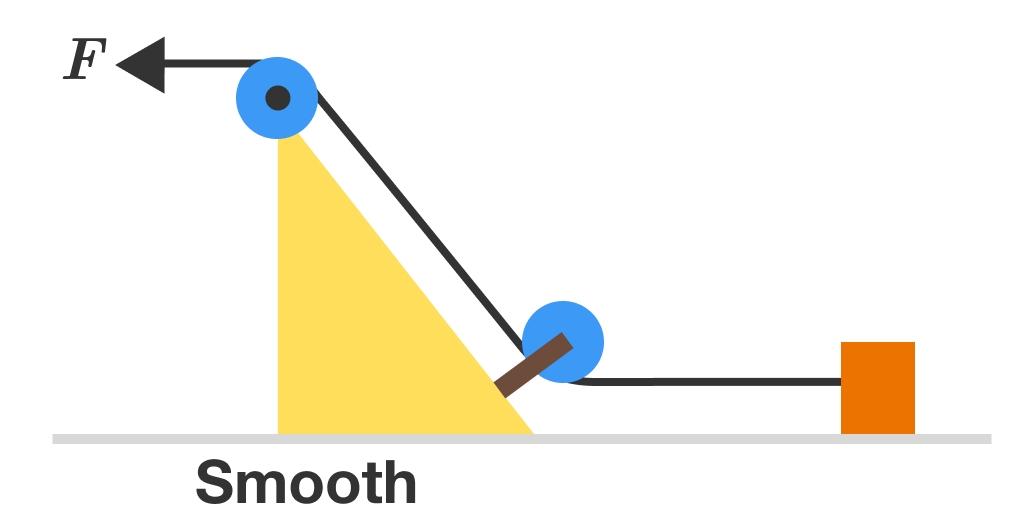
In the diagram shown below, the ground is smooth and a force of F is applied on the thread towards the left. Initially, the system was at rest. In which direction will the triangular wedge move?
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
Wouldn't the torque cause it to rotate, pivoting off of the bottom left of the wedge, moving the center of gravity to the left?
Log in to reply
Well, I suppose the corner would probably slide on the surface and the center of gravity would just go up. That change in position of the pulleys might result in the wedge going left, though... not sure.
The answer to your question depends on whether the clockwise torgue due to gravity is greater than or equal to the counterclockwise torque due to the tension in the rope.
Doh! I thought by 'wedge' they meant the orange block and that the big yellow 'wedge' with the he pulleys on was a fixed object. I see now that the orange block is an anchor.
Side note: You should edit the title. It should be confusing wedge, not confused wedge.
I think that if you set this up and try it you will be disappointed that the wedge rotates.
The image is not readable to young agers like me
We should see the normal force by rope. So it will move.
Log in to reply
You are correct, but I am afraid you missed that there are two pulleys and both are acted upon by forces of rope. Their resultant will cancel.
I believe this neglects that the tension is reduced as it passes through the pulleys because some of the force is transferred to the wedge.
Log in to reply
For the equilibrium of a thread it must posses the same tension through out.
@Rohit Gupta Since it is a non-inertial frame of reference , the pseudo force will also be acting to the right , thereby causing the triangle to move to right . Isn't it ?
Log in to reply
I am sorry, but if there is no net external force on the wedge, it will not move and become a non inertial frame in the first place.
Log in to reply
If i m not wrong ,u r saying that due to absence of frictional force and we are also not applying the external force , the whole system will still be a non-inertial frame of reference i.e. acceleration non-zero
Log in to reply
@Saraswati Sharma – The system is inertial. The wedge remains at rest. The external force is zero.
When the force F is applied, a uniform tension develops in the rope. In addition, this tension is equal to the force F that's applied. We can draw a free body diagram of the situation as follows
The rope exerts a force on each of the pulleys given by the difference of the two force vectors incident upon them. As is clear from the drawing, these two forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
Thus we can see that all the forces on the wedge cancel out so that the net force on it comes out zero. Therefore, the wedge will remain at rest.