Highly Elliptical Area
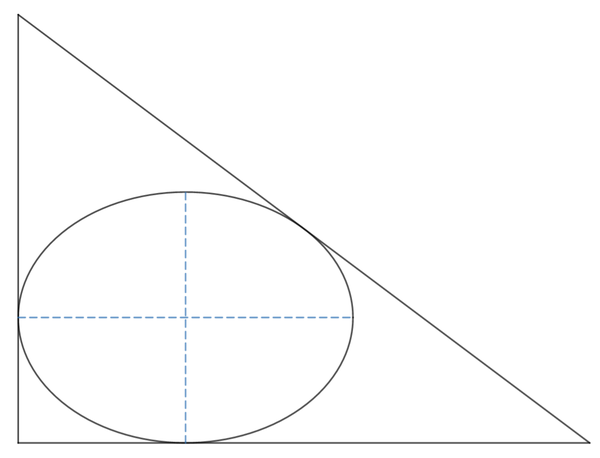
An ellipse is inscribed in a right triangle such that its major and minor axes are parallel to the perpendicular legs of the right triangle.
If the area of the ellipse is A 1 , the area of the right triangle is A 2 , and the maximum value of A 2 A 1 is π ( a − b ) , where a and b are positive integers, find a 2 + b 2 .
Try similar problems
All of my problems are original .
The answer is 73.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
We can stretch and skew the whole diagram and still preserve the ratio of areas, so we can make △ A B C an isosceles right triangle with unit legs and an area of A 2 = 2 1 ⋅ 1 ⋅ 1 = 2 1 . The ellipse will reach its maximum when it is a circle (see edit below), which also happens to be the incircle:
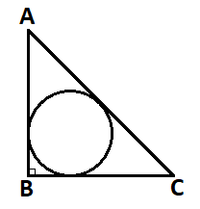
The radius of the incircle is r = s A 2 = 2 1 ( 1 + 1 + 2 2 1 = 2 1 ( 2 − 2 ) , so the area of the ellipse (or in this case circle) is A 1 = π ( 2 1 ( 2 − 2 ) ) 2 = 2 π ( 3 − 2 2 ) .
That means the ratio is A 2 A 1 = 2 1 2 π ( 3 − 2 2 ) = π ( 3 − 8 ) . Therefore, a = 3 , b = 8 , and a 2 + b 2 = 7 3 .
Edit:
A C is on y = − x + 1 and the ellipse tangent to A B and B C has an equation of a 2 ( x − a ) 2 + b 2 ( x − b ) 2 = 1 . Let ( k , − k + 1 ) on A C also be tangent to the ellipse. Then using the derivative of the equation of the ellipse, a 2 2 ( x − a ) + b 2 2 ( y − b ) d x d y = 0 or a 2 2 ( k − a ) + b 2 2 ( − k + 1 − b ) ( − 1 ) = 0 or ( − k + 1 − b ) a 2 = ( k − a ) b 2 , and since ( k , − k + 1 ) is on the ellipse, a 2 ( k − a ) 2 + b 2 ( − k + 1 − b ) 2 = 1 . These two equations solve to a = 4 k 2 k + 1 − − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 and b = 4 k − 4 2 k − 3 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 .
The area of the ellipse is A = π a b = π ⋅ 4 k 2 k + 1 − − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 ⋅ 4 k − 4 2 k − 3 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 = π ⋅ 4 k ( k − 1 ) 2 k 2 − 2 k − 1 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 . Its derivative is A ′ = 4 ( k − 1 ) 2 k 2 − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 π ( 2 k − 1 ) ( 2 k 2 − 2 k − 1 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 , and equals zero only at k = 2 1 . Since A is concave down, this is the only maximum point, so there is only one ellipse with a maximum area when k = 2 1 , which calculates to A = 2 π ( 3 − 2 2 ) .
Excellent solution sir. Thanku for sharing it with us. :)
It's important to note that the Steiner inellipse, which has the maximum area among the inscribed ellipses, goes through the midpoints of the triangle sides.
For this specific configuration, where is your proof that only the "circle" will reach the maximum value? I am not sure how you deduced that using symmetry. Please elaborate.
Log in to reply
Sir, I can't read your reply as you deleted your comment. If it is important, you could reply here. :)
Log in to reply
I accidentally deleted my comment instead of editing it. The equation will be a quadratic polynomial in a . I didn't notice there were a 2 in all of the terms.
Log in to reply
@Atomsky Jahid – No, when you'll simply, you'll see all the a 2 terms cancel out. :)
I reasoned that for every ellipse (except the circle), there will be a matching ellipse the same size (like the two ellipses below) due to the symmetry of the right isosceles triangle:
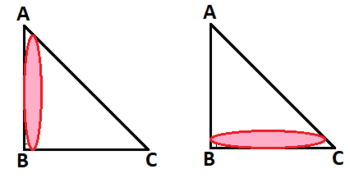
Since the question assumed a maximum, I deduced that this happened when the ellipse was a circle.
Log in to reply
But, why there can't be two ellipse with maximum area sir?
Log in to reply
@Aryan Sanghi – Hmmm. I thought one maximum was assumed by the question, but now that I'm re-reading it that may not be true. I may have to use some calculus to prove it.
Log in to reply
@David Vreken – A C is on y = − x + 1 and the ellipse tangent to A B and B C has an equation of a 2 ( x − a ) 2 + b 2 ( x − b ) 2 = 1 . Let ( k , − k + 1 ) on A C also be tangent to the ellipse. Then using the derivative of the equation of the ellipse, a 2 2 ( x − a ) + b 2 2 ( y − b ) d x d y = 0 or a 2 2 ( k − a ) + b 2 2 ( − k + 1 − b ) ( − 1 ) = 0 or ( − k + 1 − b ) a 2 = ( k − a ) b 2 , and since ( k , − k + 1 ) is on the ellipse, a 2 ( k − a ) 2 + b 2 ( − k + 1 − b ) 2 = 1 . These two equations solve to a = 4 k 2 k + 1 − − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 and b = 4 k − 4 2 k − 3 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 .
The area of the ellipse is A = π a b = π ⋅ 4 k 2 k + 1 − − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 ⋅ 4 k − 4 2 k − 3 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 = π ⋅ 4 k ( k − 1 ) 2 k 2 − 2 k − 1 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 . Its derivative is A ′ = 4 ( k − 1 ) 2 k 2 − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 π ( 2 k − 1 ) ( 2 k 2 − 2 k − 1 + − 4 k 2 + 4 k + 1 , and equals zero only at k = 2 1 . Since A is concave down, this is the only maximum point, so there is only one ellipse with a maximum area when k = 2 1 , which calculates to A = 2 π ( 3 − 2 2 ) .
Log in to reply
@David Vreken – Feels sad that such a calculation is necessary. :( I wish there could be a more elegant approach.
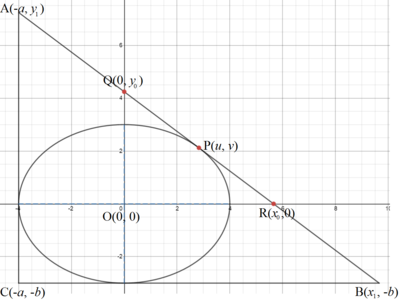
Let the ellipse be a 2 x 2 + b 2 y 2 = 1 , where a and b are the major semiaxis and minor semiaxis respectively, and the right triangle be △ A B C . To find the maximum value of A 2 A 1 is same as finding the minimum value of A 2 with the a fixed A 1 or fixed a and b . Since △ O Q R is similar to △ A B C , we can consider △ O Q R .
The gradient of a point on an ellipse is given by differentiating the equation on both sides with respect to x , a 2 2 x + b 2 2 y ⋅ d x d y = 0 ⟹ d x d y = − a 2 y b 2 x . Let the hypotenuse Q P tangent to the ellipse at P ( u , v ) . Then we have x − u y − v = − a 2 v b 2 u . Let Q ( 0 , y 0 ) and R ( x 0 , 0 ) . Then − u y 0 − v = − a 2 v b 2 u ⟹ y 0 = a 2 v b 2 u 2 + v = v b 2 ( a 2 u 2 + b 2 v 2 1 ) = v b 2 . Similarly, x 0 = u a 2 . Let u = a cos θ and v = b sin θ . Then x 0 = cos θ a and y 0 = sin θ b .
Let the area of △ O Q R be A . Then A = 2 x 0 y 0 = 2 sin θ cos θ a b = sin ( 2 θ ) a b . ⟹ A min = a b , when sin ( 2 θ ) = 1 , or θ = 4 π , or x 0 = 2 a and y 0 = 2 b .
Let A ( − a , y 1 and B ( x 1 , − b ) . By similar triangle x 0 + a y 1 = x 0 y 0 ⟹ 2 a + a y 1 = a b ⟹ y 1 = ( 1 + 2 ) b . Similarly, x 1 = ( 1 + 2 ) a . Then C A = y 1 + b = ( 2 + 2 ) b and B C = ( 2 + 2 ) a . Then A 2 min = 2 ( 2 + 2 ) 2 a b = ( 3 + 2 2 ) a b . Then we have:
A 2 min A 1 = ( 3 + 2 2 ) a b π a b = 9 − 8 π ( 3 − 2 2 ) = π ( 3 − 8 )
Then a 2 + b 2 = 3 2 + 8 2 = 7 3 (here a and b are not the semiaxes).
Excellent solution sir. Thanku for sharing it with us. :)
Let's solve using coordinate geometry
Let the perpendicular sides be coordinate axes and y = m x + c be hypotenuse.
So, if coordinates of center of ellipse are a , b , it's lengths of are also semi-major and semi-minor axes are a , b in any order.
So, equation of ellipse is
a 2 ( x − a ) 2 + b 2 ( y − b ) 2 = 1
b 2 x 2 + a 2 y 2 − 2 a b 2 x − 2 a 2 b y + a 2 b 2 = 0
Putting y = m x + c in equation
b 2 x 2 + a 2 ( m x + c ) 2 − 2 a b 2 x − 2 a 2 b ( m x + c ) + a 2 b 2 = 0
x 2 ( b 2 + a 2 m 2 ) + x ( 2 m c a 2 − 2 a b 2 − 2 a 2 b m ) + ( a 2 c 2 + a 2 b 2 − 2 a 2 b c ) = 0
As line touches the ellipse, do Discriminant D = 0
( 2 m c a 2 − 2 a b 2 − 2 a 2 b m ) 2 − 4 ( b 2 + a 2 m 2 ) ( a 2 c 2 + a 2 b 2 − 2 a 2 b c ) = 0
Solving and sumplifying above equation, we get
a = 2 m ( b − c ) c 2 − 2 b c
Now, let's minimise area of ellipse
A = π a b
A = π 2 m ( b − c ) c 2 − 2 b c b
A = 2 m π c ( b − c ) c b − 2 b 2
For minimising area,
d b d A = 0
2 m π c ( b − c ) 2 ( b − c ) ( c − 4 b ) − ( b c − 2 b 2 ) = 0
2 b 2 − 4 b c + c 2 = 0
Solving and taking smaller value as solution
b = c ( 1 − 2 1 )
Putting value of b in area expression
A = 2 m π c b ( b − c ) c − 2 b
A 1 = 2 m π c c ( 1 − 2 1 ) ( c ( 1 − 2 1 ) − c ) c − 2 c ( 1 − 2 1 )
A 1 = − 2 m π c 2 ( 3 − 8 )
Now, Finding area of triangle
A 2 = 2 1 m − c c A 2 = − 2 m c 2
Therefore
A 2 A 1 = π ( 3 − 8 )
So, a = 3 , b = 8 , a 2 + b 2 = 7 3
Visualisation: Maximum area of ellipse is about 5 3 . 9 % of triangle's area.