Inte-greater!
∫ − π / 6 π / 6 sin x − cos x sin x d x = A π + 2 1 ln ( B − C )
Given A , B and C are positive integers satisfying the equation above, find A + B + C .
The answer is 11.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
5 solutions
Same solution
Log in to reply
Great... :-)
Log in to reply
You said you'll come after JEE ADVANCED
Log in to reply
@Vignesh S – Now its not of much use since I'll be leaving brilliant in a short time. :-)
Log in to reply
@Rishabh Jain – OK... but you can still contribute when you have time
Why are you not in slack?
I ⟹ 2 I ⟹ I = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin x − cos x sin x d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin ( − x ) − cos ( − x ) sin ( − x ) d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin x + cos x sin x d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin x − cos x sin x d x + ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin x + cos x sin x d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin 2 x − cos 2 x sin x ( sin x + cos x + sin x − cos x ) d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π sin 2 x − cos 2 x 2 sin 2 x d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π − cos 2 x 1 − cos 2 x d x = ∫ − 6 π 6 π ( 1 − sec 2 x ) d x = x ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ − 6 π 6 π − 2 ∫ 0 6 π sec 2 x d x = 3 π − 2 × 2 1 ln ( tan 2 x + sec 2 x ) ∣ ∣ ∣ ∣ 0 6 π = 3 π − ln ( 3 + 2 ) + ln ( 0 + 1 ) = 3 π + ln ( 3 + 2 1 ) = 3 π + ln ( 2 − 3 ) = 6 π + 2 1 ln ( 2 − 3 ) By ∫ a b f ( x ) d x = ∫ a b f ( a + b − x ) d x
⟹ A + B + C = 6 + 2 + 3 = 1 1
You could also do the standard tangent half angle substitution.
Great solution! : )
The theorem highlighted in blue, what theorem is that?
Log in to reply
I learned it in Brilliant. Anyway, you can derive it by letting y = a + b − x . Try it.
I don't know how to do this in LaTeX but
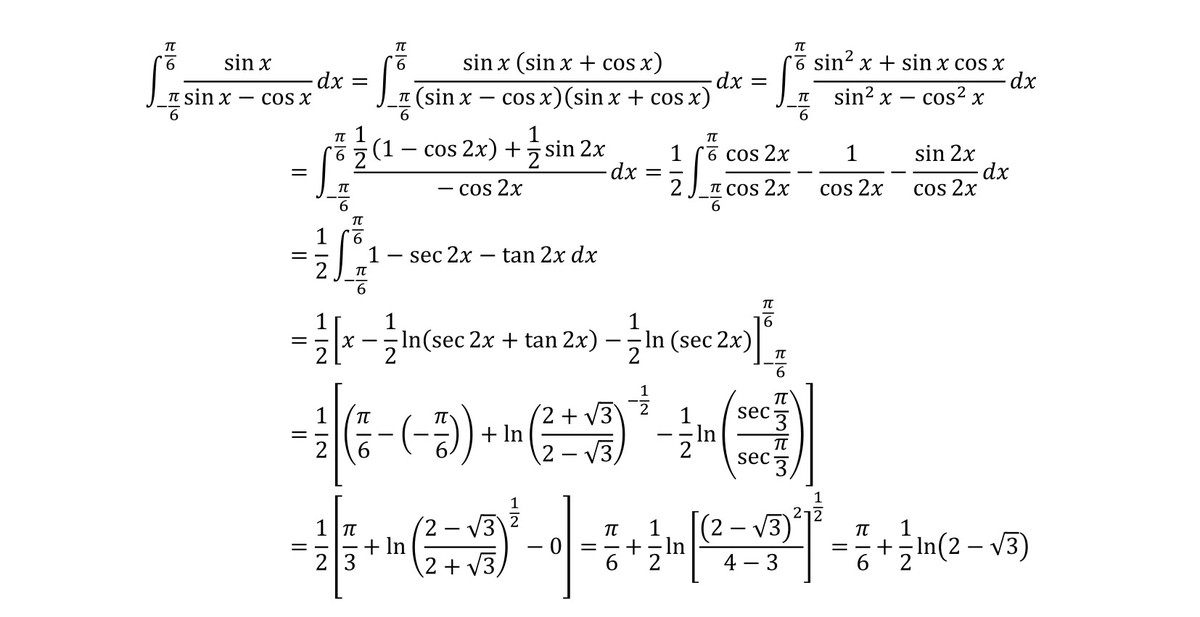 A
+
B
+
C
=
6
+
2
+
3
=
1
1
A
+
B
+
C
=
6
+
2
+
3
=
1
1
Numerator can be rewritten as 0.5(sinx-cosx)+0.5(sinx+cosx) split the denominator and use small substitution to find answer orally
split into interval -pi/6 to 0 and 0 to pi/6 . Then after basic manipulation we get 2sin^2 x in num and -cos2x in denominator .Add and subtract cos^2 x in numerator
Relevant wiki: Integration Tricks
Write numerator as 2 1 ⋅ 2 sin x = 2 1 ( ( sin x − cos x ) + ( sin x + cos x ) ) so that integration ( I ) is:
I = 2 1 ∫ − π / 6 π / 6 ⎝ ⎜ ⎜ ⎛ 1 + sin x − cos x sin x + cos x d ( sin x − cos x ) ⎠ ⎟ ⎟ ⎞ d x
= 6 π + [ 2 1 ln ∣ sin x − cos x ∣ ] − π / 6 π / 6
= 6 π + 2 1 ln ( 2 − 3 )
Hence, 6 + 2 + 3 = 1 1