Interesting Inequality 2
Find the minimum value of
4 ( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + w 2 ) + ( x y − 7 ) 2 + ( y z − 7 ) 2 + ( z w − 7 ) 2 + ( w x − 7 ) 2
as x , y , z , and w range over all real numbers.
The answer is 96.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
5 solutions
@Mark Hennings Sir can we parametrise Ellipsoid. What will be its elemental area by taking a patch d A ?? Please
Log in to reply
If we parametrize the ellipsoid as follows r = ⎝ ⎛ a cos θ b sin θ cos ϕ c sin θ sin ϕ ⎠ ⎞ then the infinitesimal normal area vector is d A = ∂ θ ∂ r × ∂ ϕ ∂ r d θ d ϕ = ⎝ ⎛ b c cos θ a c sin θ cos ϕ a b sin θ sin ϕ ⎠ ⎞ sin θ d θ d ϕ so the scalar infinitesimal area element is d A = b 2 c 2 cos 2 θ + a 2 c 2 sin 2 θ cos 2 ϕ + a 2 b 2 sin 2 θ sin 2 ϕ sin θ d θ d ϕ
Log in to reply
@Mark Hennings
Thank you so much Sir . Can you find velocity as function of time in this question
V
(
t
)
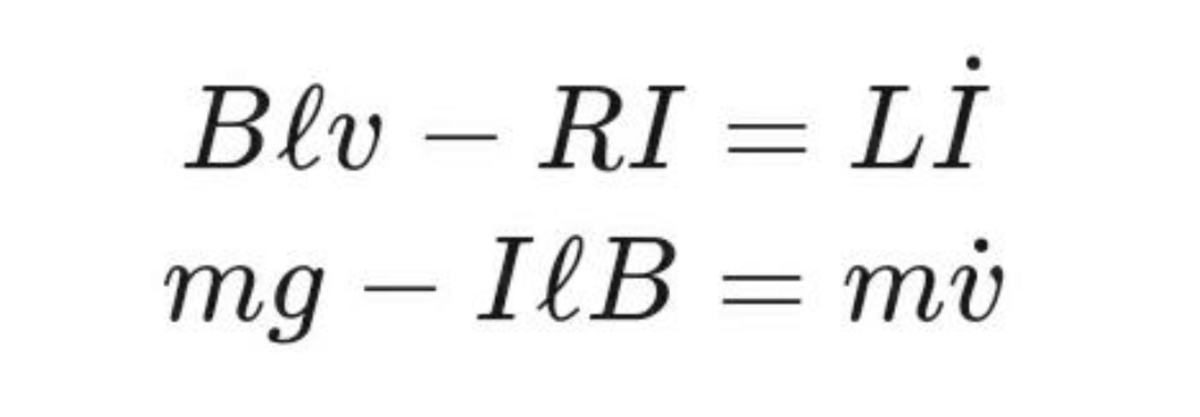 Thanks in advance!
Thanks in advance!
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Assuming B , R , ℓ , m are all constants, we can eliminate I from these equations, obtaining m L v ¨ + m R v ˙ + B 2 ℓ 2 v = m g R Obviously the particular integral is B 2 ℓ 2 m g R , but the exact form of the complementary function depends on the relative values of B , R , ℓ , m .
Log in to reply
@Mark Hennings – @Mark Hennings Yes sir, B , R , l , m all are constant. I have also reached to that differential equation but can't able to solve.
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – You need to solve for the complementary function, solving the homogeneous DE with 0 on the RHS. This equation has solutions of the form e u t provided that m L u 2 + m R u + B 2 ℓ 2 = 0 Depending on the values of B , R , m , ℓ , there may be real or complex roots, which will alter the possible behaviour of v with time.
Look up how to solve second order DEs with constant coefficients. The process of hunting for the complementary function and the particular is standard theory.
Log in to reply
@Mark Hennings – @Mark Hennings Sir I searched its standard result from everywhere as I can but didn't get. Can you search and provide me standard result ? I will be very grateful. Thanks in advance!
X = 4 ( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + w 2 ) + ( x y − 7 ) 2 + ( y z − 7 ) 2 + ( z w − 7 ) 2 + ( w x − 7 ) 2 ≥ 1 6 4 x 2 y 2 z 2 w 2 + 4 ( x y − 7 + y z − 7 + z w − 7 + w x − 7 ) 2 ≥ 1 6 x y z w + 4 ( x y + y z + z w + w x − 2 8 ) 2 ≥ 1 6 x y z w + 4 ( 4 x y z w − 2 8 ) 2 = 1 6 × 5 + 4 ( 4 × 5 − 2 8 ) 2 = 9 6 By AM-GM inequality By Titu’s lemma By AM-GM inequality Equality when x = y = z = w = 5
References:
f ( x , y , z , w ) = 4 ( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + w 2 ) + ( x y − 7 ) 2 + ( x z − 7 ) 2 + ( z w − 7 ) 2 + ( x w − 7 ) 2 Solve system
f x = x ( 8 + 2 y 2 + 2 w 2 ) − 1 4 ( w + y ) = 0
f y = y ( 8 + 2 x 2 + 2 z 2 ) − 1 4 ( x + z ) = 0
f z = z ( 8 + 2 y 2 + 2 w 2 ) − 1 4 ( w + y ) = 0
f w = w ( 8 + 2 x 2 + 2 z 2 ) − 1 4 ( x + z ) = 0
Find
x = 4 + y 2 + w 2 7 ( w + y )
y = 4 + x 2 + z 2 7 ( x + z )
z = 4 + y 2 + w 2 7 ( w + y )
w = 4 + x 2 + z 2 7 ( x + z )
From here we see x = z and y = w and m i n f ( x , y , z , w ) = m i n f ( x , y , x , y ) = m i n g ( x , y )
g ( x , y ) = 8 ( x 2 + y 2 ) + 4 ( x y − 7 ) 2
Solve system
g x = 1 6 x + 8 ( x y − 7 ) y = 0
g y = 1 6 y + 8 ( x y − 7 ) x = 0
we find
-
x = − 5 , y = − 5
-
x = 5 , y = 5
-
x = 0 , y = 0
And find min f ( x , y , z , w ) = 9 6 .
Control
d 2 g ( x , y ) = A g x x d x 2 + B g x y d x d y + C g y y d y 2 ≥ 0 for x = 5 , y = 5 .
R. M. S. - A. M. inequality :
4 ( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + w 2 ) ≥ ( x + y + z + w ) 2
( x y − 7 ) 2 + ( y z − 7 ) 2 + ( z w − 7 ) 2 + ( w x − 7 ) 2 ≥ 4 ( ( x y − 7 ) + ( y z − 7 ) + ( z w − 7 ) + ( w x − 7 ) ) 2 = 4 ( x y + y z + z w + w x − 2 8 ) 2
A. M. - G. M. inequality :
( x + y + z + w ) 2 ≥ 1 6 x y z w
x y + y z + z w + w x ≥ 4 x y z w
So, 4 ( x 2 + y 2 + z 2 + w 2 ) + ( x y − 7 ) 2 + ( y z − 7 ) 2 + ( z w − 7 ) 2 + ( w x − 7 ) 2 ≥ 1 6 x y z w + 4 ( x y z w − 7 ) 2 = 4 ( x y z w − 5 ) 2 + 9 6 ≥ 9 6
The equality holds when x = y = z = w
Hence the required minimum of the given expression is 9 6 .
I'd love to see a problem like this one where the solution isn't found at some point where all the variables have the same value, but that doesn't appear to be the case here.
If we look at the line where w = x = y = z we are basically trying to minimize the function f ( x ) = 1 6 x 2 + 4 ( x 2 − 7 ) 2 , which has a minimum at x = 5 , where its value is 9 6 . I did plug the 4-variable function into an Excel worksheet, where I tested the neighborhood of this point and satisfied myself that at least this was a local minimum.
I'd love to see an actual proof.
The expression can be rewritten as 2 [ ( x − y ) 2 + ( y − z ) 2 + ( z − w ) 2 + ( w − x ) 2 ] + ( x y − 5 ) 2 + ( y z − 5 ) 2 + ( z w − 5 ) 2 + ( w x − 5 ) 2 + 9 6 and hence the minimum value is 9 6 , achieved when x = y = z = w = 5 .