Is it geometry II?
Let x , y and z be positive real numbers such that: ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎧ x 2 + x y + y 2 = 2 5 y 2 + y z + z 2 = 1 4 4 z 2 + z x + x 2 = 1 6 9 Compute the value of ( x y + y z + z x ) 2
The answer is 4800.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
Moderator note:
Good approach using the geometric interpretation to solve this problem.
Is the condition on "positive real numbers" needed? What happens if we allow for all real numbers instead?
Nice Cheers!!!
not sure if I understand the sine rule part. how does that give you the area of the three triangles?
Log in to reply
Do you know Area of Triangles - Sine Rule ?
Log in to reply
thanks. i've probably seen it but rarely use it. i didnt remember. so it's kind of like half of the norm of the cross product, if those 2 sides were vectors. makes sense.
Log in to reply
@Aren Nercessian – Right, the determinant gives the volume of the cuboid spanned by the vectors. In the case of 2-dimensions, it gives us the parallelogram. The area of the triangle is half of that.
Log in to reply
Yes?
Log in to reply
No,i just wanted you to see this solution and comment on it.I ticked the box saying 'Do you want a challenge master to see this solution?".
Log in to reply
@Adarsh Kumar – I get the "member requested for feedback" separately. I respond to it periodically (as opposed to immediately).
Log in to reply
@Calvin Lin – Oh!Sorry for that sir.I have learnt the lesson.
First of all,we see a striking resemblance between the three equations and the cosine law as there are three square values and tow of them have been multiplied. The cosine law is c 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2 a b cos θ ,where θ is the angle opposite to the side c .Now if we compare the law and the first equation we get that c = 5 , x = a , y = b and − 2 x y × cos θ = 1 hence cos θ should be 2 − 1 which means θ = 1 2 0 ∘ .Comparing the other two equations also we get three triangles Now,seeing that all three triangles have one angle equal to 1 2 0 ∘ ,we think that they can be joined at one common vertex,doing so we get a triangle with sides, ( 5 , 1 2 , 1 3 ) which is a right-angled triangle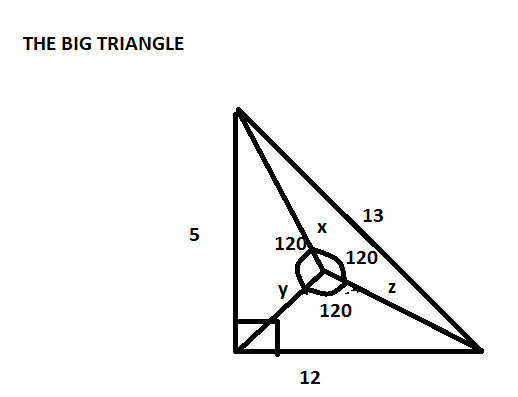
Now,the area of the big triangle would be 3 0 unit 2 which is equal to the sum of the areas of the three small triangles.Hence,we have from the sine rule that, 3 0 = 2 1 × sin 1 2 0 ∘ ( x y + y z + z x ) .From here we can easily find the answer. In response to the Challenge Master's Note: Yes,sir the condition"positive" is needed as we have taken them to be sides of the triangle. Cheers!