Can You Solve This Without Trigonometry?
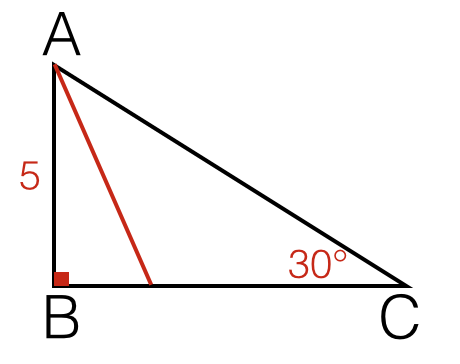 Let
A
B
C
be a triangle with
∠
B
=
9
0
∘
,
∠
C
=
3
0
∘
and
A
B
=
5
Find the length of the angle bisector from
A
to
B
C
(right to
2
decimal places).
Let
A
B
C
be a triangle with
∠
B
=
9
0
∘
,
∠
C
=
3
0
∘
and
A
B
=
5
Find the length of the angle bisector from
A
to
B
C
(right to
2
decimal places).
The answer is 5.77.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
If you take the length of BC = 12, then BD = 12-x, which means AD = 12-x. However if you put that into the Pythagorean theorem (5^2 + x^2 = (12-x)^2), it would give you a value of x=4.96 which obviously isn't possible given the hypotenuse of a right triangle must be the longest side. any idea why this approach doesn't work?
Log in to reply
It should work too, but you put the angle bisector as 1 2 − x while its value is x .
apply 30 60 90 theorem
I used CAH here. Is that allowed?
Log in to reply
I don't get it at all... What do you call CAH?
Log in to reply
Cos 30 = Adj/ Hyp
Log in to reply
@Felix Castrillon – But that's trigonometry.... it's not allowed
There's another way there, i have observe 2 equal proportions
How do we go from knowing that A B D is similar to A B C (but rotated), to knowing that 2 x 3 = 5 → x = 3 1 0 3 .
My initial response is to try to use Pythagorean Theorem; however, I only know the one side. Trig is considered "off limits" (and besides, it isn't currently fresh and geometry is pre-requisite).
Can we get the value without trig
i guess u are taking the angle bisector. however if u take the edge (BC) bisector, the value of AD will be 6.614
Why is angle DAB 30 degrees?
Log in to reply
As ∠ A = 6 0 ° and A D is the bisector, we have ∠ D A B = 2 ∠ A = 3 0 °
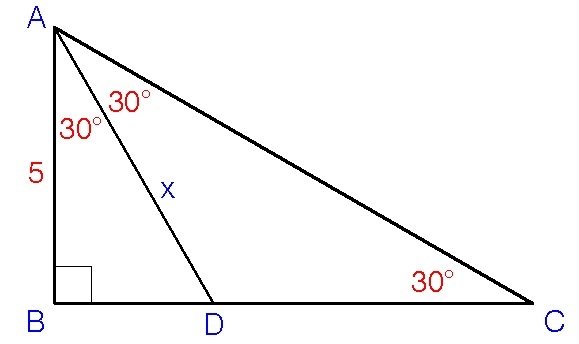 We know that
∠
A
=
6
0
∘
. Divide this into two equal angles (see my figure). Let
x
be the length of the angular bisector. Then,
We know that
∠
A
=
6
0
∘
. Divide this into two equal angles (see my figure). Let
x
be the length of the angular bisector. Then,
cos 3 0 ∘ = h y p o t e n u s e a d j a c e n t s i d e = x 5 ⟹ x = cos 3 0 ∘ 5 ≈ 5 . 7 7
when I say "Without Trig" I mean without trigonometry xD
Hey Bro even I found it in the same way
This is my own solution using my old account. I have a new account now.
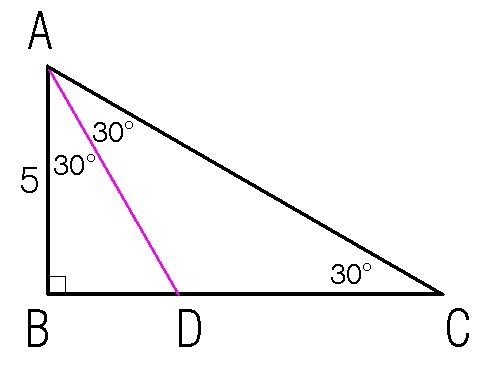 Using Trigonometry(CAH):
c
o
s
=
h
y
p
a
d
j
Using Trigonometry(CAH):
c
o
s
=
h
y
p
a
d
j
Let A D be the length of the angular bisector. Since it is right triangle, ∠ B A C = 9 0 − 3 0 = 6 0 ∘ . We divide it by 2 , we get: ∠ D A C = ∠ B A D = 3 0 ∘ . Then,
c o s 3 0 = A D 5
A D = c o s 3 0 5 = 5 . 7 7 answer correct to two decimal places
First we have that ∠ A = 6 0 o , and the bisector intersects B C at D . As ∠ D A B = 3 0 o → ∠ A D B = 6 0 o this means, if the bisector equals x we have 2 x 3 = 5 → x = 3 1 0 3