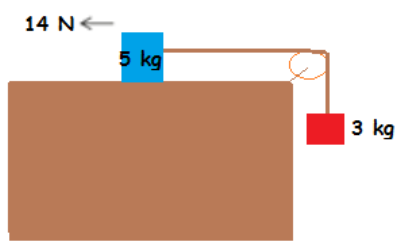
It May Weigh Less
A constant force of
1
4
N
is applied on the
5
kg
block. Will the
3
kg
block move up or down or will it remain at rest?
Try my World of Physics to solve many problems like this one.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
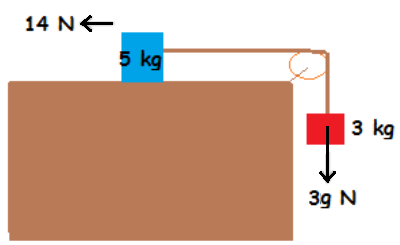 Besides the applied
1
4
N
, there is another external force due to the weight of the hanging
3
kg
block, which is
F
1
=
3
g
N
, where
g
≈
1
0
ms
−
2
is the acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore, the downward acceleration
a
1
due to
F
1
is given by
F
1
=
(
3
+
5
)
a
1
=
3
g
⟹
a
1
≈
8
3
0
=
3
.
7
5
ms
−
2
.
The upward acceleration
a
due to the
1
4
N
force is
(
3
+
5
)
a
=
1
4
⟹
a
=
8
1
4
=
1
.
7
5
ms
−
2
.
Since the downward acceleration
a
1
is much larger than the upward acceleration
a
, assuming insignificant friction between the
5
kg
block and the table top and between the rope and pulley, and the rope is light weight, the
3
kg
block will move
down
.
Besides the applied
1
4
N
, there is another external force due to the weight of the hanging
3
kg
block, which is
F
1
=
3
g
N
, where
g
≈
1
0
ms
−
2
is the acceleration due to gravity.
Therefore, the downward acceleration
a
1
due to
F
1
is given by
F
1
=
(
3
+
5
)
a
1
=
3
g
⟹
a
1
≈
8
3
0
=
3
.
7
5
ms
−
2
.
The upward acceleration
a
due to the
1
4
N
force is
(
3
+
5
)
a
=
1
4
⟹
a
=
8
1
4
=
1
.
7
5
ms
−
2
.
Since the downward acceleration
a
1
is much larger than the upward acceleration
a
, assuming insignificant friction between the
5
kg
block and the table top and between the rope and pulley, and the rope is light weight, the
3
kg
block will move
down
.
Ram Mohith , the k of kg should be in lowercase for SI units. You have missed a "t" for "rest" in the end.
Log in to reply
Thank you sir. I modified it.
Log in to reply
Again no space before "?".
Log in to reply
@Chew-Seong Cheong – Grammatically there shouldn't be a space before a sentence and its punctuation.
Log in to reply
@Krishna Karthik – I was asking Ram not to add a space before "?".
IMO you should specify that it is a frictionless surface, because in reality this surface would have friction and there would not be enough information to answer the question.