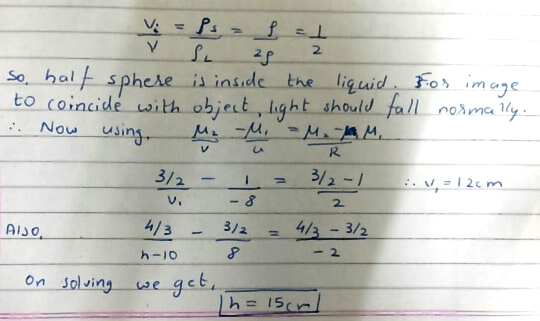Optics... #1
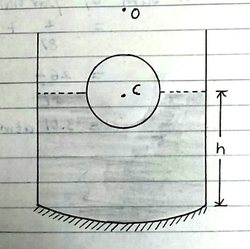 A transparent solid sphere of radius
2 cm
, and density
floats in a transparent liquid of density
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with radius of curvature
8 cm
and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in the above figure. When an object is placed at a distance of
10 cm
directly above the centre of the sphere C, its final image coincides with it. Find
h
(as in figure), the height of the liquid surface in the in the beaker from the apex of the bottom. Consider the paraxial rays only.
A transparent solid sphere of radius
2 cm
, and density
floats in a transparent liquid of density
kept in a beaker. The bottom of the beaker is spherical in shape with radius of curvature
8 cm
and is silvered to make it a concave mirror as shown in the above figure. When an object is placed at a distance of
10 cm
directly above the centre of the sphere C, its final image coincides with it. Find
h
(as in figure), the height of the liquid surface in the in the beaker from the apex of the bottom. Consider the paraxial rays only.
A paraxial ray is a ray that makes a small angle to the optical axis of the system, and lies close to the axis throughout the system.
Refractive index of sphere is .
Refractive index of liquid is .
Round that answer to nearest integer .
h is measured in cm
To try more such problems click here .
The answer is 15.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.