Oxygen - Carbon Bond Counter
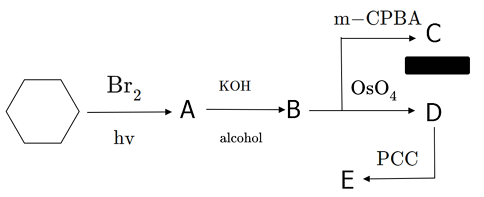
Starting with cyclohexane, proceed through the series of reactions shown above. For products C , D , and E ; count the total number of C − O (carbon to oxygen) bonds in each molecule. In the image above, m-CPBA stands for meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid and PCC stands for pyridinium chlorochromate.
You answer should be the sum of the C − O bonds in products C , D , and E .
Note : Be careful of certain groups; for example, a ketone will count as two C − O bonds. Same is true for epoxides. And of course, carboxylic acids will contain three.
David's Organic Chemistry Set
David's Physical Chemistry Set
The answer is 8.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Let me elaborate a bit.
All hydrogens are similar in cyclohexane hence by free radical substitution reaction you will get 1-bromo-cyclohexane . (Have you ever thought of the role of hv in free radical substitution?) it is used in the initiation of reaction that is to break Br2 molecules homolytically to form radicals)
Then you have Alcoholic KOH .that is E2 Elimination (Bimolecular elimination) . Its free of rearrangement and proceeds through a transition state.
Also it is called bimolecular reaction because the rate of reaction depends on Concentration of substrate (Alkyl halide) as well as that of reagent (Alcoholic KOH) that is reaction follows second order kinetics.
Next for C You have syn hydroxylation reaction of Alkene. Note that It follows syn stereochemistry because two hydroxyl groups are added from same side. the other reagenet we could have used apart from Osmium tetraoxide is Cold Alkaline Potassium Permanganate .(Dont use Hot here because that will yield a different product)
From D To E You have Oxidation of Alcohol . Note that 3 degree alcohols do not get oxidised due to absence of alpha hydrogen .
So Alcohol will get Oxidised To Ketone here . Well the main use Of PCC is to prevent the oxidation of primary alcohols completely to carboxylic acids and stop the reaction at aldehyde stage
Now from B To C You have syn epoxidation of alkene . but notice that Epoxides are unstable because 3 membered rings are very unstable due to high angle strain. So if we would have added a little acid or base ring would have opened quite easily!!.
Nice problem again !:)
Once again, you have given an incredible explanation. Thank you!
once again, you have given an incredible explanation. Thank you!
Log in to reply
tu kyon copy kar rha hai @David Hontz ka comment?
Log in to reply
mera key board khrab h screen pe likhna pdta h
kl mera janam din h :)
Log in to reply
ohh cool! . subah 10:30 to 1:30 mast gift milega tujhe :P
Log in to reply
thnku aur agar english mein mast no. aage toh gift hi h :) btw best of luck for english :P
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Thanks same 2 u . i will give my best wishes tomorrow on ur birthday
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – will wait till then abhi toh padle invisible man :P
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Happy birthday bhai! may god bless you and give all things you want! stay blessed bro
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – aaaahhhhhhhh................akhirkar :P my waiting seems fruitful now :P kaisa hua english ka ppr ?
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Badiya tera?
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – pehle to pel diya , 1 ghante pehle ho gya tha , phir khali bheta rha, physics ka kya socha h ? mai soch ra hu ki saari derivation aaj hi kr leta" https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-derivations-in-class-12-physics-in-the-CBSE-Board " , bhai aache no. aane chahiye 12 ke finals h :)
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – badiya badiya!
@A Former Brilliant Member – thnx bhai, tu bhi kar le derivation ! :P
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Bohot time h . JEE Is my target ultimately
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – sahi bat h bhai mujhe b lagta h jyatatar to aati h , akhri Q plz .... brilliant pe Q solve kr ra h ya module ?
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Nothing . mock tests
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – thnku bhai for giving inspiration ......i will study more and try to reach ur lvl nd i don't need slack if we can talk slightly here , mai kl wo Q publish krunga jo muhjse hue ni plz try :) :)
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – yep we can talk here no problem! :)
@A Former Brilliant Member – i will try :)
@A Former Brilliant Member – ok :P :P :P
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – bhai hogi tyar ?
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – kya pata result aaega tab pata chalega :P
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – chal 1 Q poochta hu wo bta diya to maan junga ...........which method was used by evans to stop the clotting of pig blood ? :P
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Ye nhi aane wala 3 number mein itni detail mein nhi jaaenge . basic story pata honi chahiye bas
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – na aaye to hi aachaa h :P phir bhi aa gya toh 1/10th volume of 3.8 % trisodium citrate :)
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Abe english ka exam h . pichle saal ka paper dekh asan question aae h. wo story puchna chahte h evans wala chapter saala waise he itna lamba h :P
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – english k ppr se jyada b'day ki excitement h :P
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Wo to hogi hi bhai! :)
Log in to reply
@Prakhar Bindal – best of luck bro..........abhi school ke hawan mei jana h :P
C − O b o n d s P r o d u c t C : 2 ( e p o x i d e ) P r o d u c t D : 2 ( d i o l ) P r o d u c t E : 4 ( d i o n e ) Total C-O bonds : 8