Story of Chrome and Flux
A particle with mass
m
and charge
q
=
1
C
is placed at
(
1
,
−
8
0
,
0
)
, is launched at
t
=
0
at an angle
θ
=
4
5
°
(
θ
is taken from the line
x
=
1
m
in the upward direction, when you see the launching of particle from
−
x
direction seeing toward
+
x
direction you will see the angle
θ
in the clockwise direction) with a speed of
v
=
4
0
m
/
s
.
A chrome figure is placed in
Y
−
Z
plane .
 The centre of the chrome has the coordinates
(
0
,
0
,
4
0
)
.
Let the flux passing through blue area is
ϕ
B
and through white area is
ϕ
W
and similarly for all surfaces.
The total radius of chrome is
2
m
and total radius of blue disc
1
m
and width of white region is
0
.
2
m
.
Evalute the value of expression at
t
=
2
2
s
e
c
(
ϕ
B
+
ϕ
W
+
ϕ
Y
+
ϕ
R
+
ϕ
G
ϕ
B
ϕ
W
ϕ
Y
ϕ
R
ϕ
G
)
1
0
6
Details and Assumtion
g
=
1
0
m
s
−
2
,
ϵ
0
=
1
The centre of the chrome has the coordinates
(
0
,
0
,
4
0
)
.
Let the flux passing through blue area is
ϕ
B
and through white area is
ϕ
W
and similarly for all surfaces.
The total radius of chrome is
2
m
and total radius of blue disc
1
m
and width of white region is
0
.
2
m
.
Evalute the value of expression at
t
=
2
2
s
e
c
(
ϕ
B
+
ϕ
W
+
ϕ
Y
+
ϕ
R
+
ϕ
G
ϕ
B
ϕ
W
ϕ
Y
ϕ
R
ϕ
G
)
1
0
6
Details and Assumtion
g
=
1
0
m
s
−
2
,
ϵ
0
=
1
The answer is 0.589.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
1 solution
@Steven Chase Sir Fast and Accurate solution. But sir if the position of charge is not symmetrical. Then how can we find the flux??
Log in to reply
It can still be done, but it is much less trivial. The geometry of those three regions would have to be explicitly given. Probably the best way would be to specify the start and end points of the three line segments.
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase Sir your new question of RLC. Can I find I m i n with pen and page. Does it need numerical resolution which I don't know how to do?
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – It probably requires numerical simulation. But if you derive the state-space (which isn't too hard to do), the numerical integration part is easy. There are many examples of it in the solutions that have already been posted.
@Steven Chase in your new question I am getting both I S 0 and I S ∞ as 1 0 A .
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Yes, that's correct
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase
–
@Steven Chase
By solving these
6
equation and minimizing
i
1
+
i
2
we will reach the answer.
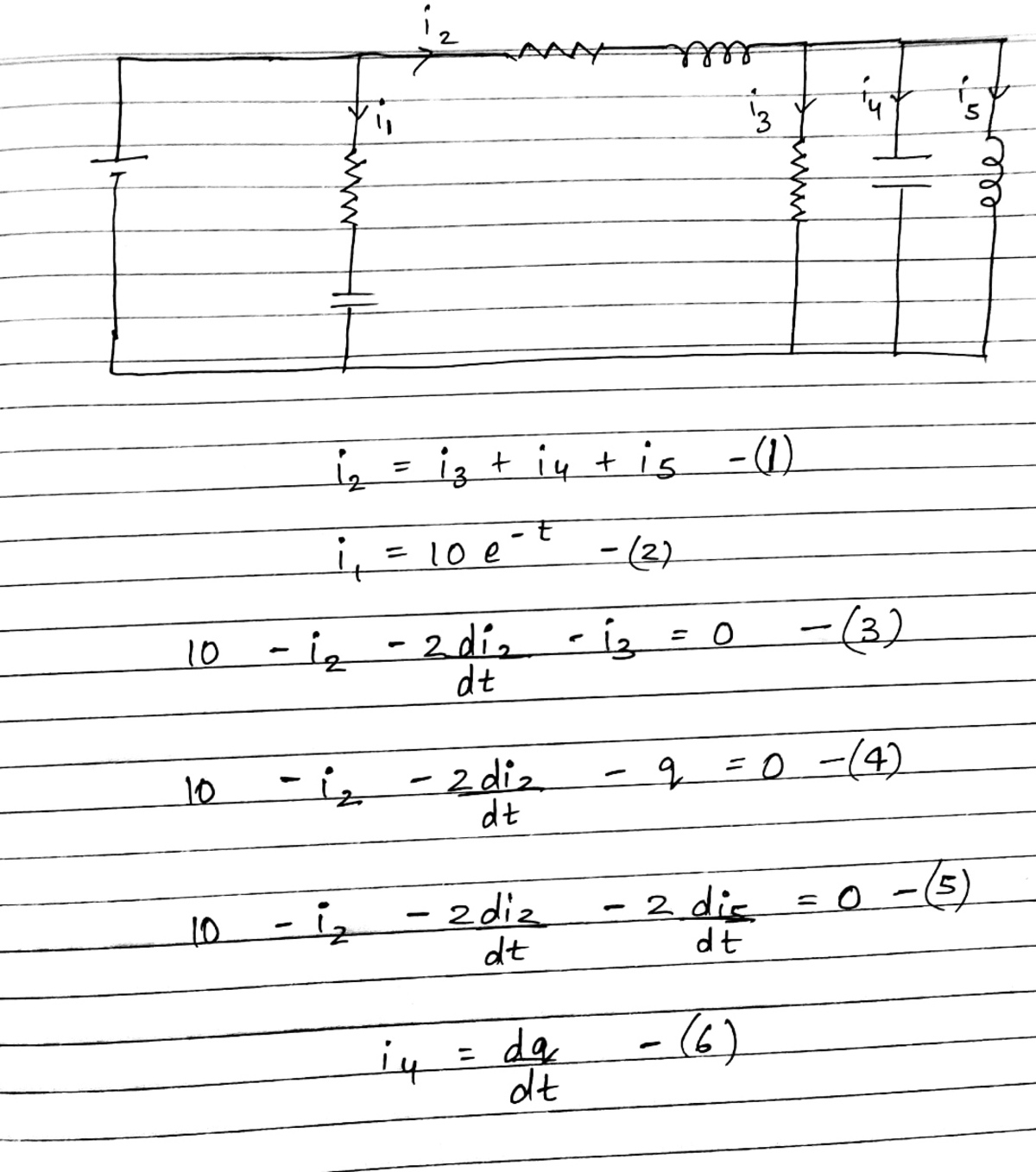 Am I right???
Am I right???
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – Everything you have here looks correct.
I am planning to post a simplified version of the asymmetrical problem
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase Ok I am interested and Ready!
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – The new problem is up now. I will post a note about my profile image later
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase – @Steven Chase Sir I have uploaded the solution of that problem. When you will post a note of profile image?? Can you post it today. Because I want to upload it somewhere else not on brilliant.
Log in to reply
@A Former Brilliant Member – I'll post it within the next hour or so
@Steven Chase Sir from where you get that image of your profile photo of brilliant?Can you share the link of photo. I will not copy and upload it. I like that photo and will upload somewhere else.
@Steven Chase Sir i was making a question but not able to solve. The question is that a charged particle ( q = 1 c ) is moving in the line z = 1 moving towards the + x axis with a speed 1 m s − 1 . A loop is placed at x 2 + y 2 = 1 Find the rate of current induced in the loop. How can we solve this ?? Please help.
@Steven Chase
I will post my solution later. Here are 3 different analytical methods.


@Steven Chase Did you enjoyed all these 3 methods?
Log in to reply
All three are interesting. Method 1 is the standard diff eq approach, and the other two are very creative.
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase Yes. I have uploaded the solution of electric Field and plate (part 2 ) solution by a trick. Hope you liked that trick.
@Steven Chase
Sir please help me in this problem.
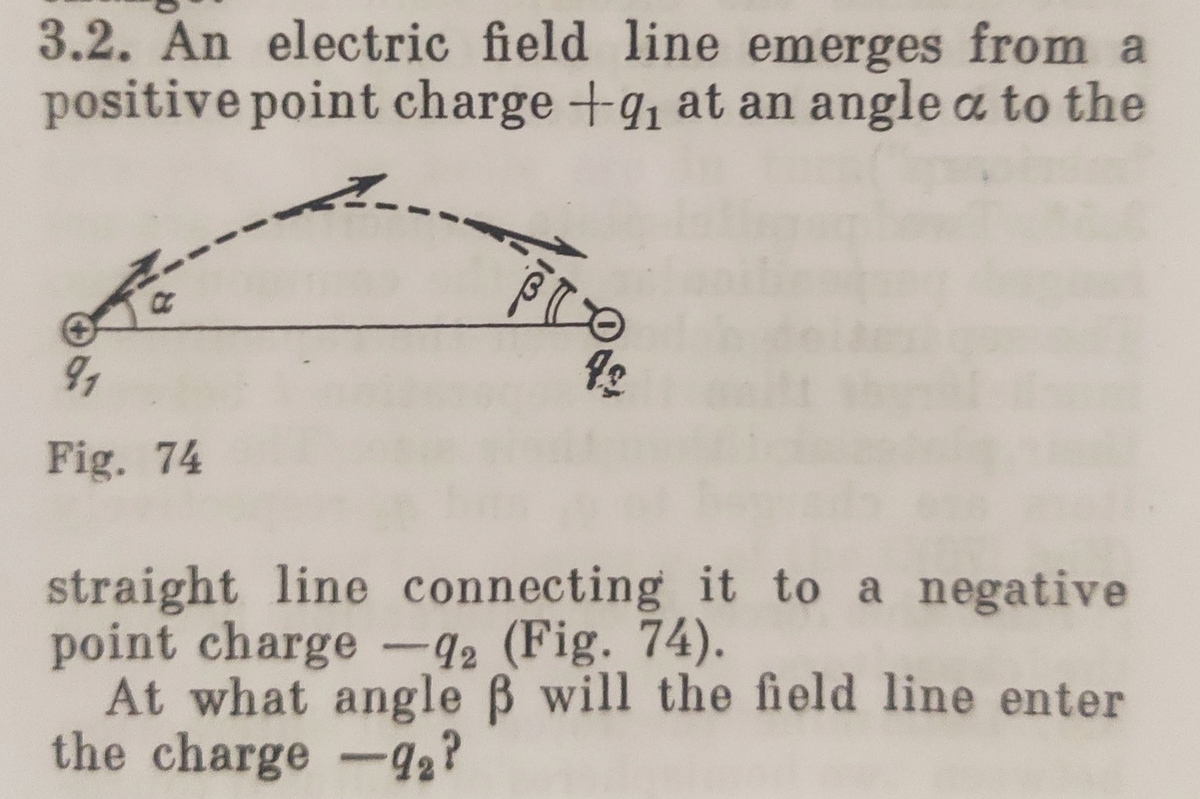
Thanks in advance
Check out the solutions to this problem https://brilliant.org/problems/electric-angle/
Log in to reply
@Steven Chase but why it is necessary that all the flux which passes through the circle will go to that another charge??
@Steven Chase I have made a question in my mind ,a infinte long wire carry current in sinusoidal form. A ring is placed 1m aprt from that wire. Calculte the I(t) in that ring. How is this question. You can post it.
That sounds like a good one. You can post it
Working out the kinematics puts the charge a distance of 1 unit directly above the center of the disk. From there, it is a standard flux calculation. I formulated it as a double integral, although it could have been done as a single integral. Since the problem is symmetrical, we need not concern ourselves with the exact geometry of the yellow, red, and green regions. All that matters is that those three regions have identical fluxes. For convenience, I considered the disk to be in the x y plane, with the charge being on the z axis.