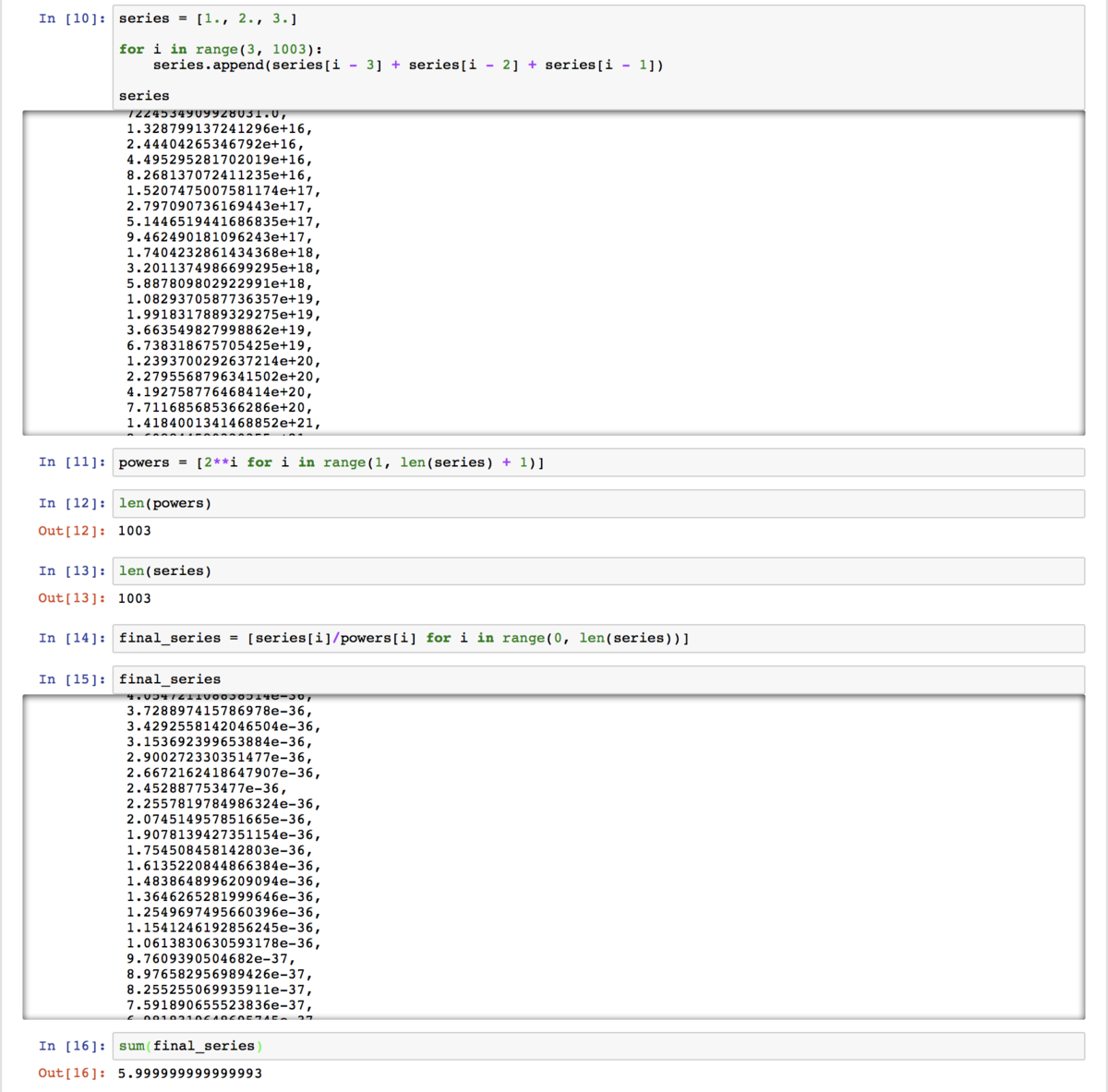
What type of sequence is this?
Find the value of S as defined below:
S = 2 1 + 2 2 2 + 2 3 3 + 2 4 6 + 2 5 1 1 + 2 6 2 0 + 2 7 3 7 + 2 8 6 8 + ⋯
Enter 666 if you come to the conclusion that the series fails to converge.
Note that the numerators follow the pattern T n + 3 = T n + 2 + T n + 1 + T n .
The answer is 6.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
3 solutions
How do you know that the series converges in the first place?
Log in to reply
I found it the same way as you did sir... Generating Functions
Log in to reply
But your work does not show that. Your work assumes that the series converges in the first place when you say : "We have our original sequence S = ..."
If you had considered 0.6 instead of 0.5, your answer would come out wrong.
Fair warning: One of these days I will submit a problem where your approach gives the wrong answer ;)
Log in to reply
@Otto Bretscher – Sir, i made this problem after Finding the range of value of x for which the Series Converges , The problem is already hard , i don't want to make it harder by saying " series is Converging or not ? " It is understood that the Series is converging if i am not mentioning it.
Log in to reply
@Sabhrant Sachan – The convergence is the interesting part; the rest is trivial algebraic manipulation. It is the main point of generating functions that they let you easily find the radius of convergence.
I like the problem, though!
Log in to reply
@Otto Bretscher – Thanks sir. I like The concept of Generating Functions.It help us in These type of Series, in Calculating the Number of Integral Solutions of a equation ... and even more .
Log in to reply
@Sabhrant Sachan – To make the solvers think about convergence, you could add something like "Enter 666 if you come to the conclusion that the series fails to converge." It would make the problem even more interesting.
I like your problems! They are varied, thought-provoking and often entertaining. Keep posting!
@Otto Bretscher – I will be looking forward to Face the challenge .
The numerators form the Tribonacci numbers with T n + 3 = T n + 2 + T n + 1 + T n for n > 0 . The generating function is found to be ∑ n = 1 ∞ T n x n = 1 − x − x 2 − x 3 x ( 1 + x ) for ∣ x ∣ < 0 . 5 4 . For x = 2 1 the value is 6
We have our original Sequence : S = 2 1 + 2 2 2 + 2 3 3 + 2 4 6 + 2 5 1 1 + 2 6 2 0 + 2 7 3 7 + 2 8 6 8 . . . ∞ Equation 1: − 2 1 S = − 2 2 1 − 2 3 2 − 2 4 3 − 2 5 6 − 2 6 1 1 − 2 7 2 0 − 2 8 3 7 − 2 9 6 8 . . . ∞ Equation 2: − 2 2 1 S = − 2 3 1 − 2 4 2 − 2 5 3 − 2 6 6 − 2 7 1 1 − 2 8 2 0 − 2 9 3 7 − 2 1 0 6 8 . . . ∞ Equation 3: − 2 3 1 S = − 2 4 1 − 2 5 2 − 2 6 3 − 2 7 6 − 2 8 1 1 − 2 9 2 0 − 2 1 0 3 7 − 2 1 1 6 8 . . . ∞ Now add These Three Equations , You get : S ( − 2 1 − 2 2 1 − 2 3 1 ) = − 2 2 1 − 2 3 3 − 2 4 6 − 2 5 1 1 − 2 6 2 0 − 2 7 3 7 − 2 8 6 8 . . . ∞ Add This Equation and the Original Equation, We get : S ( 1 − 2 1 − 2 2 1 − 2 3 1 ) = 2 1 + 2 2 1 S = 1 − 0 . 5 − 0 . 2 5 − 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 5 + 0 . 2 5 S = 0 . 1 2 5 0 . 7 5 = 6