Three is Four
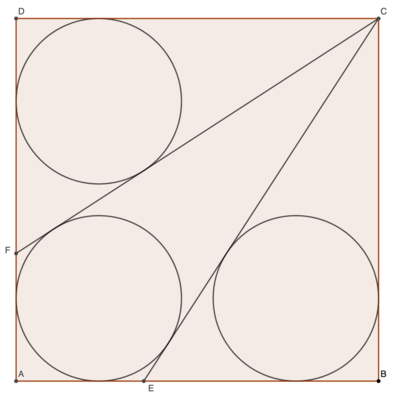
The figure shows three congruent circles in the unit square, A B C D . Find a closed-form for the length of their radius, r , convert it to decimal, and submit ⌊ 1 0 6 r ⌋ .
The answer is 228155.
This section requires Javascript.
You are seeing this because something didn't load right. We suggest you, (a) try
refreshing the page, (b) enabling javascript if it is disabled on your browser and,
finally, (c)
loading the
non-javascript version of this page
. We're sorry about the hassle.
2 solutions
Very clear explanation (and diagram). Nice observation about the excircle. Thank you.
Log in to reply
Your kind comments/remarks are always appreciated :)
Log in to reply
@Fletcher Mattox I think you meant to write three "congruent" circles (not three "concentric" circles) in the problem.
The half-angle tangent substitution provide a straight-forward way of solving incircle problems as shown in this solution.
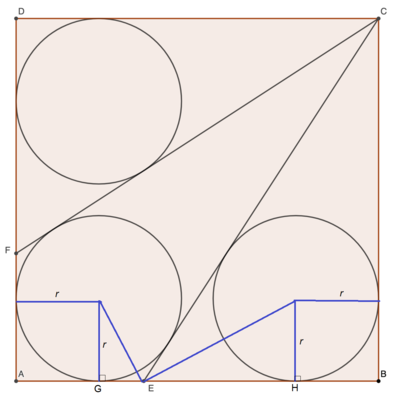
Let ∠ C E B = θ . Consider the bottom-right circle and segment E B .
E H + H B r cot 2 ∠ C E B + r r cot 2 θ + r t r + r t 1 + t ⋅ r r ⟹ t = E B C B cot ∠ C E B = cot θ = 2 t 1 − t 2 = 2 t 1 − t 2 = 2 1 − t = 1 − 2 r Let t = tan 2 θ
Now consider A B :
r + r cot ( 9 0 ∘ − 2 θ ) + r cot 2 θ + r 2 r + r t + t r 2 r t + r t 2 + r 2 r ( 1 − 2 r ) + r ( 1 − 2 r ) 2 + r 4 r 3 − 8 r 2 + 6 r − 1 = A B = 1 = 1 − t = 1 − 2 r = 0 Note that t = 1 − 2 r Using Cardano’s method
⟹ r ⟹ ⌊ 1 0 6 r ⌋ = 3 2 − 3 3 3 3 3 − 1 7 1 + 6 3 3 3 3 − 1 7 ≈ 0 . 2 2 8 1 5 5 4 9 3 6 5 3 9 6 2 = 2 2 8 1 5 5
Reference: Cardano's method
Construction: Extend line segments C F , B A and let G be the point of intersection.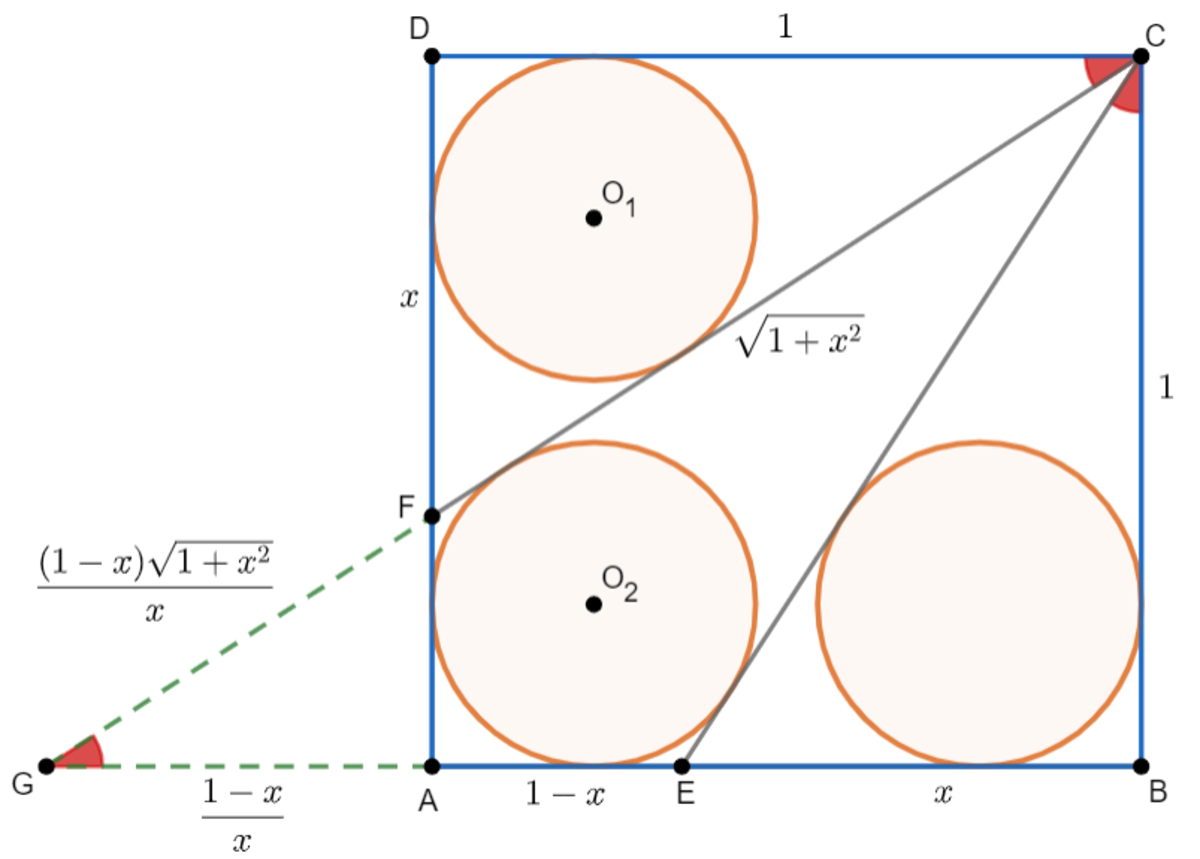 Since
△
D
C
F
∼
△
A
G
F
,
A
F
F
D
=
G
A
C
D
⟹
1
−
x
x
=
G
A
1
⟹
G
A
=
x
1
−
x
Using the Pythagorean Theorem in
△
D
C
F
and
△
A
G
F
,
C
F
2
C
F
F
G
2
F
G
=
F
D
2
+
D
C
2
=
1
+
x
2
=
G
A
2
+
A
F
2
=
x
2
(
1
−
x
)
2
+
(
1
−
x
)
2
=
x
(
1
−
x
)
1
+
x
2
The circle centered at
O
1
is the
incircle
of right
△
D
C
F
. Therefore,
r
=
C
D
+
D
F
+
F
C
C
D
⋅
D
F
=
1
+
x
+
1
+
x
2
x
The circle centered at
O
2
is the
excircle
of right
△
A
G
F
. Therefore,
r
=
G
A
+
F
G
−
A
F
G
A
⋅
A
F
=
x
1
−
x
+
x
(
1
−
x
)
1
+
x
2
−
(
1
−
x
)
x
1
−
x
⋅
(
1
−
x
)
=
1
+
1
+
x
2
−
x
1
−
x
So, we have the following relations,
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎧
r
=
1
+
x
+
1
+
x
2
x
r
=
1
+
1
+
x
2
−
x
1
−
x
Solving the above system of equations, we have,
x
≈
0
.
6
4
7
7
9
8
8
.
.
.
,
r
≈
0
.
2
2
8
1
5
5
4
.
.
.
⟹
⌊
1
0
6
r
⌋
=
2
2
8
1
5
5
Since
△
D
C
F
∼
△
A
G
F
,
A
F
F
D
=
G
A
C
D
⟹
1
−
x
x
=
G
A
1
⟹
G
A
=
x
1
−
x
Using the Pythagorean Theorem in
△
D
C
F
and
△
A
G
F
,
C
F
2
C
F
F
G
2
F
G
=
F
D
2
+
D
C
2
=
1
+
x
2
=
G
A
2
+
A
F
2
=
x
2
(
1
−
x
)
2
+
(
1
−
x
)
2
=
x
(
1
−
x
)
1
+
x
2
The circle centered at
O
1
is the
incircle
of right
△
D
C
F
. Therefore,
r
=
C
D
+
D
F
+
F
C
C
D
⋅
D
F
=
1
+
x
+
1
+
x
2
x
The circle centered at
O
2
is the
excircle
of right
△
A
G
F
. Therefore,
r
=
G
A
+
F
G
−
A
F
G
A
⋅
A
F
=
x
1
−
x
+
x
(
1
−
x
)
1
+
x
2
−
(
1
−
x
)
x
1
−
x
⋅
(
1
−
x
)
=
1
+
1
+
x
2
−
x
1
−
x
So, we have the following relations,
⎩
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎧
r
=
1
+
x
+
1
+
x
2
x
r
=
1
+
1
+
x
2
−
x
1
−
x
Solving the above system of equations, we have,
x
≈
0
.
6
4
7
7
9
8
8
.
.
.
,
r
≈
0
.
2
2
8
1
5
5
4
.
.
.
⟹
⌊
1
0
6
r
⌋
=
2
2
8
1
5
5